Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
A uniform sphere of mass 2-kg and radius 1.0 meters is accelerated from rest. The final velocity of the center of mass is 3.0 m/s , and the final angular velocity of the sphere is 2 radians/sec . What is the total work done on the sphere ? Assume the sphere is solid .a. 9 J
b. 10.6 J
c. 1.6 J
d. 7.4 J
e. 0 J
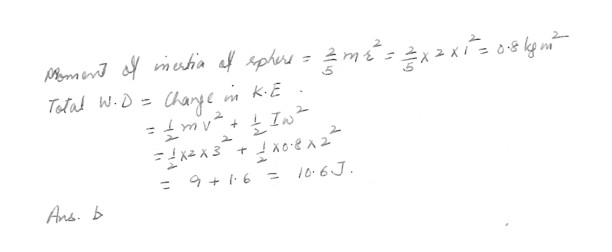
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
A man raises a 60-kg sack a distance of 1.5 meters to his shoulder , carries it for a distance of 300 meters along a level road and then lowers it to the ground . How much total work does gravity do ?a. 883 J
b. 0 J
c. -883 J
d. 90 J
e. -90 J
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
Potential energy is defined for which type(s) of forces ?a. Spring force .
b. Any non-conservative force .
c. Gravitational force .
d. Any conservative force .
e. All of the above .
f. Any force of type a ,c , or d .
g. Any force of type b ,c ,or d .
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
A meteorite strikes the Earth perpendicularly at a speed of 10^3 m/s . If the mass of the meteorite is 10^3 kg and the mass of the Earth is 6 x 10^24 kg , What is the magnitude of the change in the velocity of the Earth ?a. 1.29 x 10^-8 m/s
b. 1.67 x 10^-19 m/s
c. 1.67 x 10^-25 m/s
d. Since the collision is inelastic , the Earth does not change its velocity .
e. Since the collision is inelastic , momentum is not conserved and the velocity change cannot be calculated .
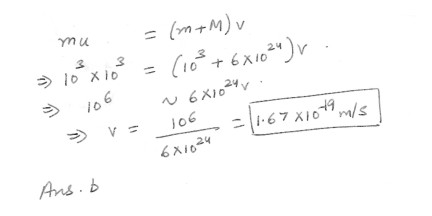
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
Suppose that two masses , consulting an isolated system are involved in a collision. Prior to the collision, mass ,m , has a speed of 10 m/s and mass , m , is at rest . After the collision , m has a speed of 6 m/s and m’ has a speed of 8 m/s . The masses of the two bodies are equal . What can be said about the collision ?a. It conserves momentum .
b. It does NOT conserve momentum .
c. If conserves energy .
d. Both a and c are true .
e. Both b and c are true .
f. All of the above are true .
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
In an experiment , two balls of equal radii and different masses are dropped from a height 20-m above the ground . Both balls hit the ground at the same time . Which of the following statements BEST describes the potential energies of the two balls before they are dropped ?a. The ball with the smaller mass has greater potential energy .
b. The ball with the larger mass has the greater potential energy .
c. Both have the same potential energy .
d. The value of potential energy CANNOT be determined until a zero potential energy level is selected .
e. Based on d , either a , b , or c may be true .
f. None of the above are true .
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
For the pendulum shown , one can MOST accurately find the speed of the bob at the bottom of its arc by using :a. delta è /delta t = -omega èmax sin(omega t + indefinite )
b. Conservation of linear momentum .
c. Conservation of angular momentum .
d. Conservation of mechanical energy .
e. Conservation of Torque .
f. All of the above .
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
What criteria must be met for a system if total energy (defined as kinetic and potential ) is conserved ?a. The center of mass of the system moves with constant acceleration .
b. The sum of all internal forces equals zero .
c. The sum of all external torque is zero .
d. The sum of all external forces is zero .
e. Only conservative forces do work .
f. Only b ,c or d are correct .
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
Potential energy is defined for which type(s) of forces ?a. Spring force .
b. Any non-conservative force .
c. Gravitational force .
d. Any conservative force .
e. All of the above .
f. Any force of type a , c , or d .
g. Any force of type b ,c ,or d .
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
Can Archimedes principle be used to measure the density of a solid object ? Can it be applied to the problem of measuring the density of a fluid ? Write an equation that will handle these two problems ?
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
A bug move radially outward on a spinning 45 rpm record . How do its angular speed and tangential speed change as it moves to larger radii ?
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
Two automobiles of equal mass approach an intersection . One vehicle is traveling with velocity 13.0 m/s toward the east , and the other is traveling north with speed V2i . Neither driver sees the other . The vehicles collide in the intersection and stick together , leaving parallel skidmarks at an angle of 55.0 degrees north of east . The speed limit for both roads is 35 mi/h , and the driver of the northward-moving vehicle claims he was within the speed limit when the collision occurred . Is he telling the truth ?
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
A 9.0 kg fullback running east with a speed of 5.00 m/s is tackled by a 95.0 kg opponent running north with a speed of 3.00 m/s . If the collision is perfectly inelastic ,(a) Calculate the speed and direction of the players just after the tackle
(b) Determine the mechanic energy lost as a result of the collision . Account for the missing energy .
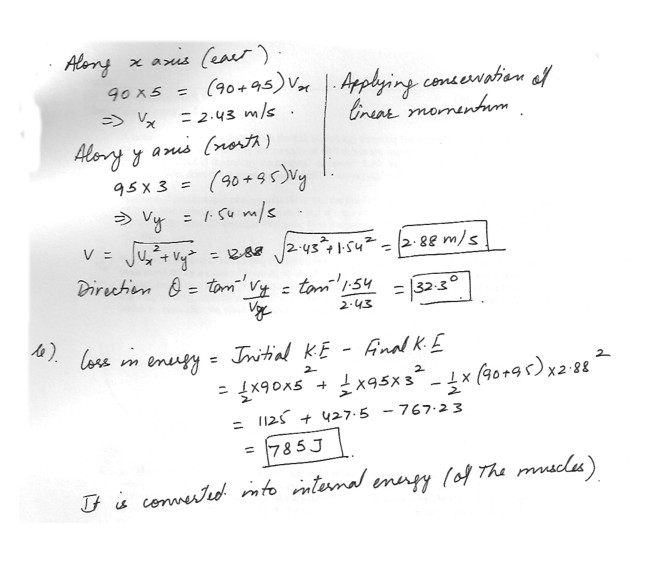
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
(a) Three carts of masses 4.00 kg , 10.0 kg and 3.00 kg moves on a frictionless horizontal track with speeds of 5.00 m/s , 3.00m/s and 4.00 m/s as shown in the figure at “click here” . Velcro couplers make the carts stick together after colliding . Find the final velocity of train of three carts .(b) Does your answer require that all the carts collide and stick together at the same time ? What if they collide in a different order ?

Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
High-speed stroboscopic photographs show that the head of a golf club of mass 200g is traveling at 55.0 m/s just before it strikes a 46.0 g golf ball at rest on a tee . After the collision , the club head travels (in the same direction) at 40.0 m/s . Find the speed of the golf ball just after impact .
