Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: High School
Demonstrate the Newton’s third law is true by taking an example from real life . Then explain how Newton’s third law applies in those situations .
Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: High School
In the ideal apparatus shown in the diagram, at “click here” , m1 = 2.0 kg . What is m2 if both masses are rest ? How about if both masses are moving at constant velocity ?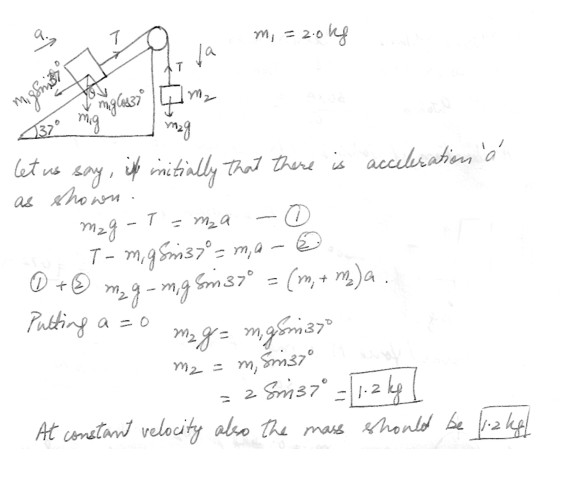
Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: High School
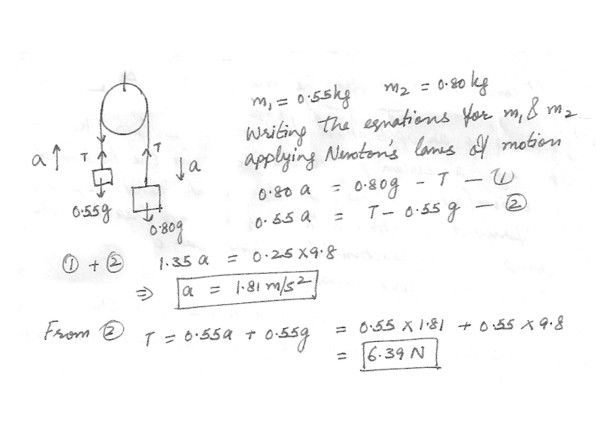
The Atwood machine consists of two masses suspended from a fixed pulley . It is named after British scientist George Atwood (1746-1807) , who used it to study motion and to measure the value of g. If m1 = 0.55 kg and m2 = 0.80 kg ,(a) What is the acceleration of the system
(b) What is the magnitude of the tension in the string
Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: High School
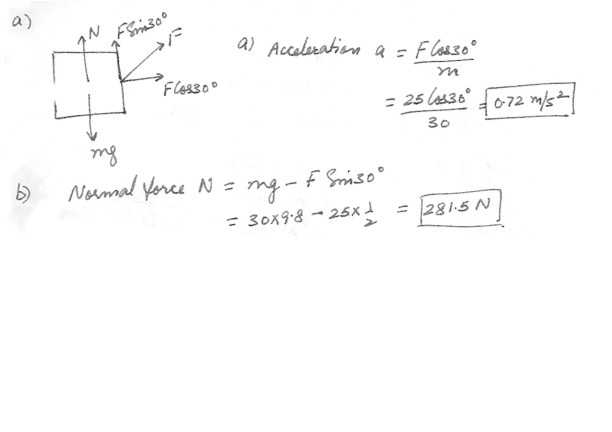
A boy pulls box of mass 30 kg with a force of 25 N in the direction shown in the figure at “click here”.(a) Ignoring friction of the box , what is the acceleration of the box ?
(b) What is the normal force exerted on the box by the ground ?
Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: High School
Jane and John , with masses if 50 kg and 60 kg , respectively , stand on a frictionless surface 10 m apart . John pulls on a rope that connects him to Jane , giving Jane an acceleration of 0.92 m/s^2 . At what rate will John accelerate ? What is the direction of his acceleration ?
Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: High School
“Newton’s second law also explains why all objects in free fall have the same acceleration . “Do you agree with this statement ? Why ? or why not ?
Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: High School
In an emergency stop to avoid an accident , a shoulder -strap seat belt holds a 60-kg passenger firmly in place . If the car were initially traveling at 90 km/h and came to a stop in 5.5 s along a straight , level road , what was the average force applied to the passenger by the seatbelt ?
Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: High School
In a college homecoming competition , 16 students lift a sports car . While holding the car off the ground, each student exerts an upward force of 400 N .(a) What is the mass of the car in kilograms
(b) What is the weight in pounds ?

Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: High School
A 1.5 kg object moves up the y-axis at a constant speed . when it reaches the origin, the forces F1 = 5.0 N at 37 degree above the +x-axis, F2 = 2.5 N in the +x-direction, F3 = 3.5 N at 45 degree below the –x-axis , and F4 = 1.5 N in the –y direction are applied to it .(a) Will the object continue to move along the y-axis ?
(b) If not , what simultaneously applied force will keep it moving along the y-axis at a constant speed ?

Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: High School
Conservation of linear momentum
A 2115 kg car traveling at 11.8 m/s collides with a 3075 kg car that is initially at rest at a spotlight . The cars stick together and move 1.94 m before friction causes them to stop . Determine the coefficient of kinetic friction between the cars and the road , assuming that the negative acceleration is constant and all wheels on both cars lock at the time of impact .
Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: High School
Conservation of linear momentum
A 2115 kg car traveling at 11.8 m/s collides with a 3075 kg car that is initially at rest at a spotlight . The cars stick together and move 1.94 m before friction causes them to stop . Determine the coefficient of kinetic friction between the cars and the road , assuming that the negative acceleration is constant and all wheels on both cars lock at the time of impact .
Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: High School
Conservation of linear momentum
High speed stroboscopic photographs show that the head of a 218 g golf club is traveling at 59.4 m/s just before it strikes a 45.6 g golf ball at rest on a tee . After the collision the club head travels (in the same direction) at 38.2 m/s . Find the speed of the golf ball just after impact .
Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: High School
Conservation of linear momentum
(a) A 0.420 kg ice puck, moving east with a speed of 3.16 m/s , has a head-on collision with a 0.940 kg puck initially at rest . Assuming a perfectly elastic collision , what is the speed of the lighter puck ? Use east as the positive axis .(b) What is the speed of the heavier puck ?

Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: High School
Conservation of linear momentum
A 2.85 kg sphere makes a perfectly inelastic collision with a second sphere that is initially at rest . The composite system moves with a speed equal to one fifth the original speed of the 2.85 kg sphere . What is the mass of the seconds sphere ?
Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: High School
Conservation of linear momentum
An 83.0 kg astronaut is working on the engines of his spaceship , which is drifting through space with a constant velocity . The astronaut , wishing to get a better view of the Universe , pushes against the ship and later finds himself 34.5 m behind the ship and moving so slowly that he can be considered to be at rest . Without a thruster , the only way to return to the ship is to throw his 0.504 kg wrench directly away from the ship . If he throws the wrench with a speed of 21.8 m/s , how many seconds does it take him to reach the ship ?
