Physics Ray Optics Level: High School
Convex Mirror
A spherical Christmas tree ornament is 8.92 cm in diameter . What is the magnification of the image of an object placed 10.5 cm away from the ornament ?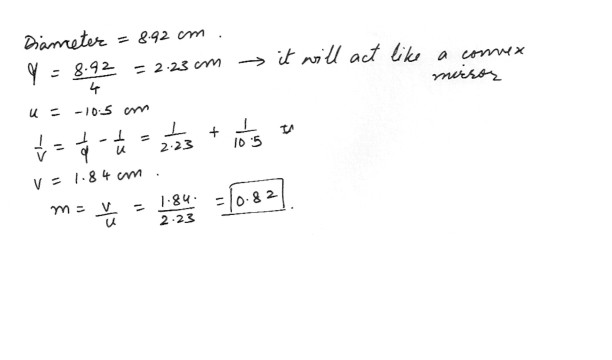
Physics Ray Optics Level: High School
Image formation by Concave Mirror
A density uses a concave mirror (focal length 3.1 cm) to examine some teeth . If the distance from the object to the mirror is 1.5 cm , what is the magnification of the tooth ?
Physics Ray Optics Level: High School
Image formation by Concave Mirror
For a concave mirror , when the object is placed closer to the mirror than the focal length of the mirror (02) in front or the mirror
3) behind the mirror
Physics Ray Optics Level: High School
Image formation by Concave Mirror
For a concave mirror , when the object is placed closer to the mirror than the focal length of the mirror (02) at infinity or undetermined
3) erect
Physics Ray Optics Level: High School
Image formation by Concave Mirror
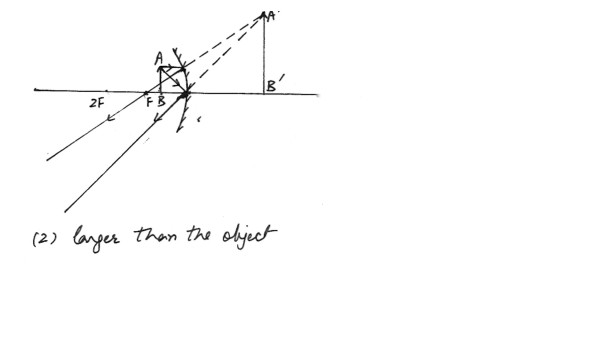
For a concave mirror , when the object is placed close to the mirror than the focal length of the mirror (02) larger than the object
3) smaller than the object
Physics Ray Optics Level: High School
Image formation by Concave Mirror
For a concave mirror, when the object is placed farther from the mirror than the mirror’s radius (R2) at infinity or non-existence .
3) behind the mirror .
Physics Ray Optics Level: High School
Image formation by Concave Mirror
For a concave mirror, when the object is placed farther from the mirror than the mirror’s radius (R2) at infinity or undetermined
3) inverted
Physics Ray Optics Level: High School
Image formation by Concave Mirror
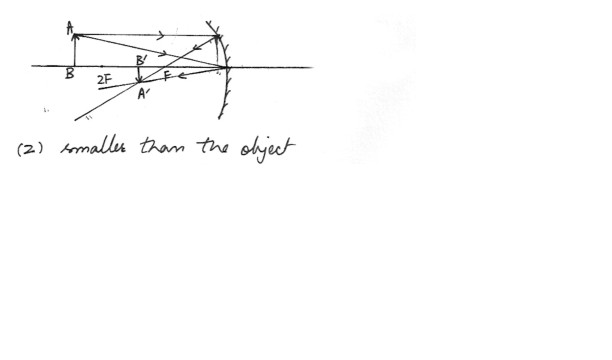
For a concave mirror, when the object is placed farther from the mirror than the mirror’s radius (R2) smaller than the object .
3) same size as the object .
Physics Ray Optics Level: High School
Image formation by Concave Mirror
For a concave mirror, when the object is placed farther from the mirror than the mirror’s focal length , but to the mirror than the mirror’s radius (I2) in front of the mirror
3) at infinity or non-existence
Physics Ray Optics Level: High School
Image formation by Concave Mirror
For a concave mirror , when the object is placed farther from the mirror than the mirror’s focal length , but closer to the mirror than the mirror’s radius (I2) erect
3) at infinity or undermined
Physics Ray Optics Level: High School
Image formation by Concave Mirror
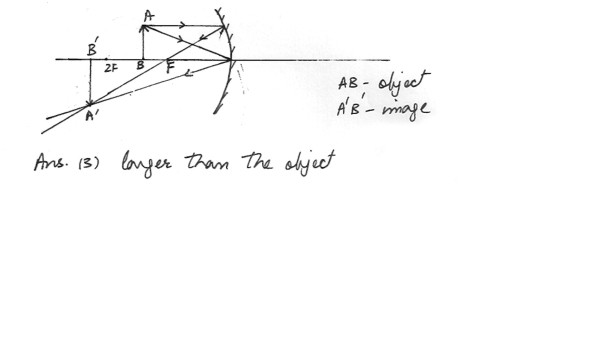
For a concave mirror , when the object is placed farther from the mirror than the mirror’s focal length , but closer to the mirror than the mirror’s radius (I2) same size as the object
3) larger than the object .
Physics Ray Optics Level: High School
Image formation by Concave Mirror
A concave mirror with a radius of curvature of 1.0 m is used to collect light from a distant star . What is the distance between the mirror and the image of the star ?1) d = 0.25 m
2) d = 2.0 m
3) d = 0.50 m
4) d = 0.75 m
5) d = 1.0 m
Physics Ray Optics Level: High School
Which of the following has the lowest frequency ?1) red light
2) x-rays
3) gamma rays
4) violet light
5) radio waves
6) microwaves
Physics Ray Optics Level: High School
Which of the following is a typical wavelength for visible light ?1) 1500 nm
2) 500 nm
3) 50 nm
4) 100 nm
5) 1000 nm
Physics Ray Optics Level: High School
Total Internal Reflection
Light traveling from medium 1 undergoes total internal reflection at the boundary to the medium 2 . What can be said about the velocity of light in medium 1 , vi, compared to the velocity of light in medium 2, t>2 ? (c is light velocity in vacuum)1. v1>v%
2. v i = v%
3. vi 4. Cannot be determined . 5. v1>c

