Physics Rotational Mechanics Level: High School
Rotational Equilibrium
A 1200 N uniform boom is supported by a cable perpendicular to the boom , as seen in the figure at “click here” . The boom is hinged at the bottom , and a m = 2060 N weight hangs from its top . Assume the angles to be alpha = 64.4 degrees and theta = 90.0 degrees – alpha . Find the tension in the supporting cable .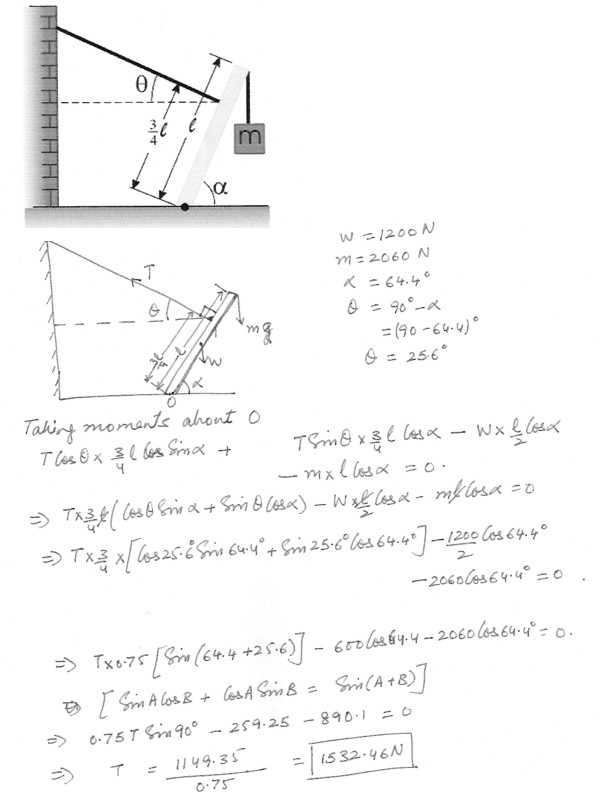
Physics Rotational Mechanics Level: High School
Rotational Equilibrium
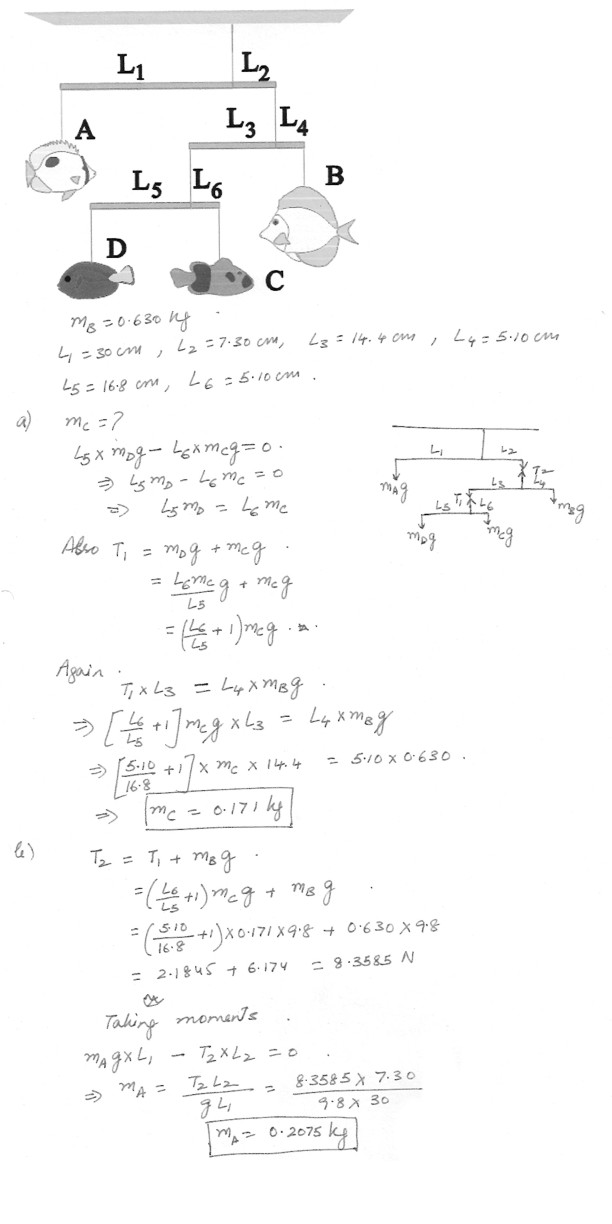
The mobile in the figure at “click here” is in equilibrium . The object B has mass of 0.630 kg .a) Determine the mass of object C . Assume L1 = 30.0 cm , L2 = 7.30 cm , L3 = 14.4 cm , L4 = 5.10 cm , L5 = 16.8 cm and L6 = 5.10 cm . (Neglect the weights of the crossbars .)
b) Determine the mass of the object A .
Physics Rotational Mechanics Level: High School
Rotational Equilibrium
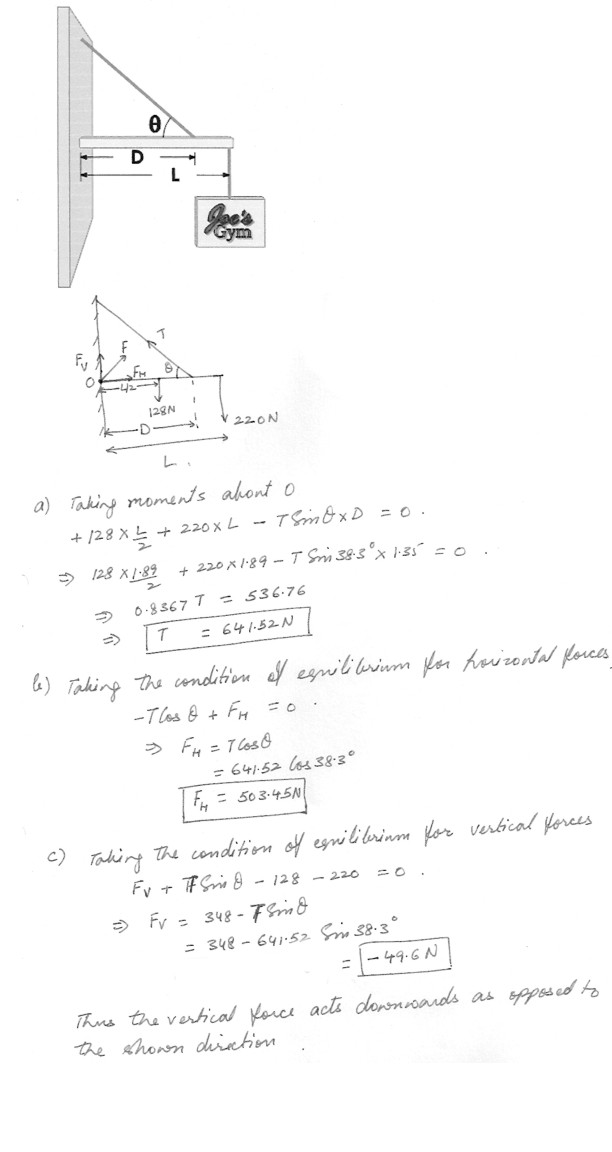
A shop sign weighing 220 N is supported by a uniform 128 N beam of length L = 1.89 m as shown in the figure at “click here” . The guy wire is connected D = 1.35 m from the backboard .a) Find the tension in the guy wire . Assume theta = 38.3 degrees .
b) find the horizontal force exerted by the hinge on the beam .
c) Find the vertical force exerted by the hinge on the beam . Use “up” as the positive direction .
Physics Rotational Mechanics Level: High School
Rotational Equilibrium
Three boys are trying to balance on a seesaw , which consists of a fulcrum rock as a pivot at the center , and a very light board L = 3.66 m long , see figure at “click here” . Two boys are already on either end . One has a mass of m1 = 44.0 kg , and the other a mass of m2 = 30.8 kg . How far from the center should the third boy , whose mass is m3 = 26.8 kg . place himself so as to balance the seesaw ?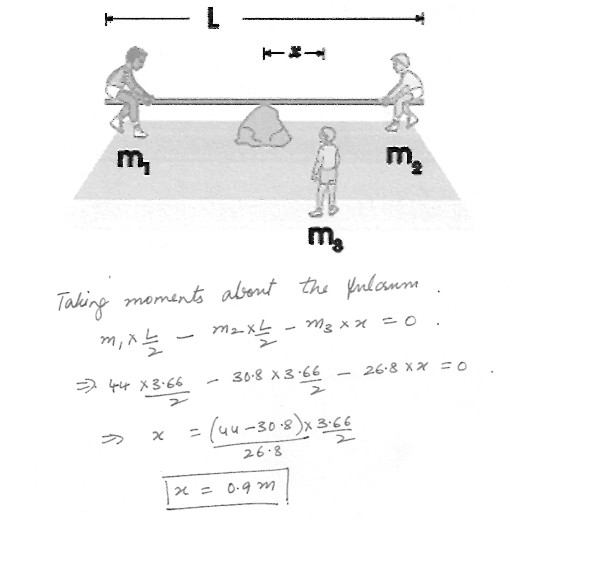
Physics Rotational Mechanics Level: High School
Rotational Equilibrium
A uniform m = 14.2 N picture frame is supported as shown in the figure at “click here” .The length of the frame is L = 32.2 cm , the width is W = 14.7 cm and assume the angle is alpha = 53.3 degrees .a) Find the tension in cord T1 .
b) Find the tension in the cord T2 .
c) Calculate the magnitude of the horizontal force at m that is required to hold the frame in the position shown .

Physics Rotational Mechanics Level: High School
Rotational Equilibrium
The arm in the figure which is shown at “click here” weighs 42.6 N . The force of gravity acting on the arm acts through point A . Assume that L1 = 0.0730 m , L2 = 0.335 m and infinite = 10.4 degrees .a) Determine the magnitude of the tension force F1 in the deltoid muscle .
b) Determine the magnitude of the tension force Fs of the shoulder on the humerus (upper-arm bone) to hold the arm in the position shown .
c) Determine the angle of tension force Fs relative to the x-axis .

Physics Rotational Mechanics Level: High School
Rotational Equilibrium
Calculate the mass m needed in order to suspend the leg shown in figure at “click here”. Assume the leg (with cast) has a mass of 13.0 kg , and its CG is 37.0 m from the hip joint ; the sling is 77.2 cm from the hip joint .
Physics Rotational Mechanics Level: High School
Rotational Equilibrium
In the figure which is shown at “click here” are seven situations where a student is holding a meter stick at the left end at various angles . A 1.0 kg mass is hung on the meter sticks at different locations . The meter stick is held stationary in all cases . All of the meter sticks are identical , but the distance along the meter stick at which the 1.0 kg mass is hung and the angles at which the student holds the meter stick vary . Specific values are given in each figure . (Ignore the mass of the meter stick.) Which of the following statements are true about the situations depicted in the figures above ?a) The torque is the same in all situations .
b) The lever arm is the same in picture B and C .
c) The net force acting on the meter stick in picture G is larger than in picture C .
d) The lever arm in picture A is : L/2 .
e) The meterstick is harder to hold in picture A than in picture B .

Physics Rotational Mechanics Level: High School
Balancing a Meter Stick
A meter stick is found to balance at the 45.0 cm mark when placed on a fulcrum . When a 46.0 g mass is attached at the 12.6 cm mark , the fulcrum must be moved to the 35.2 cm mark for balance . What is the mass of the meter stick ?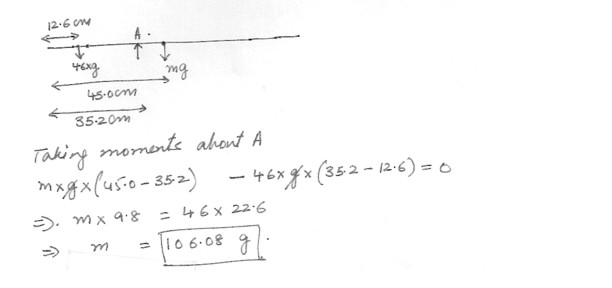
Physics Rotational Mechanics Level: High School
Rotational Equilibrium
A window washer with a mass of 73.0 kg stands a distance , D = 0.800 m , from the left end of a plank of length , L = 1.90 m ,with a mass of 17.0 kg . The plank is hung on two cables . Find T2, the tension in the right cable .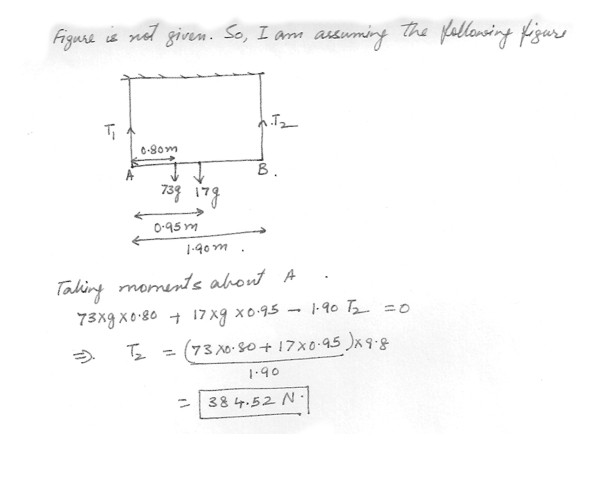
Physics Rotational Mechanics Level: High School
In the figure which is shown at “click here” , the cylinder and pulley turn without friction about stationary horizontal axles that pass through their centers . A light rope is wrapped around the cylinder , passes over the pulley , and has a 3.00 kg box suspended from its free end . There is no slipping between the rope and the pulley surface . The uniform cylinder has mass 5.00 kg and radius 40.0 cm . The pulley is a uniform disk with mass 2.00 kg and radius 20.0 cm . The box is released from rest and descends as the rope upwraps from the cylinder . Find the speed of the box when it has fallen 1.50 m .
Physics Rotational Mechanics Level: High School
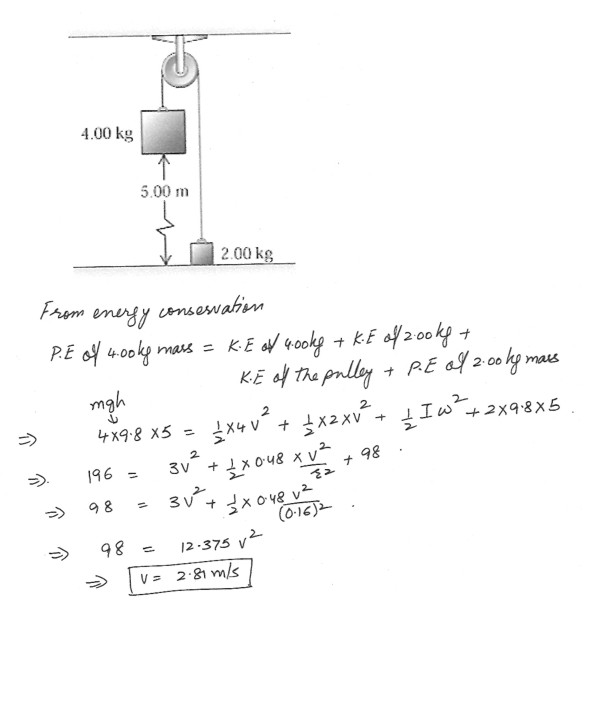
The pulley in the figure which is shown at “click here” has a radius 0.160 m and a moment of inertia 0.480 kg.m^2 . The rope does not slip on the pulley rim .a) Use energy methods to calculate the speed of the 4.00 kg block just before it strikes the floor .
Physics Rotational Mechanics Level: High School
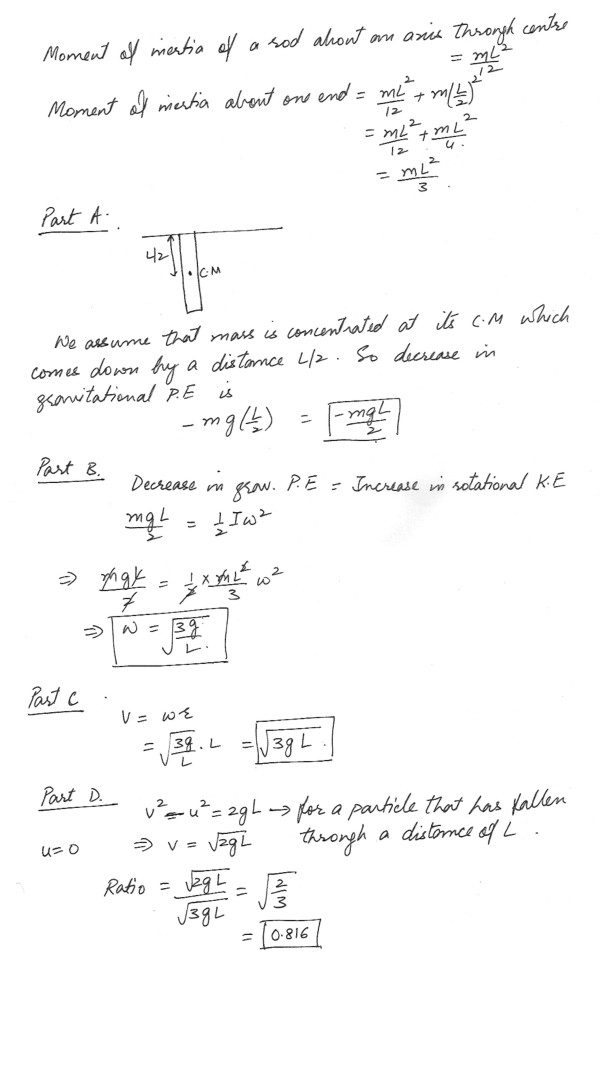
A stick with a mass ‘m’ and a length of ‘L’ is pivoted about one end so it can rotate without friction about a horizontal axis . The meter stick is held in a horizontal position and released .a) As it swings through the vertical , calculate the change in gravitational potential energy that has occurred . (Use ‘g’ for the acceleration due to gravity )
b) As it swings through the vertical , calculate the angular speed of the stick .
c) As it swings through the vertical , calculate the linear speed of the end of the stick opposite the axis .
d) Find the ratio of the speed of a particle that has fallen a distance of ‘L’ , starting from rest , to the speed from part (C) .
Physics Rotational Mechanics Level: High School
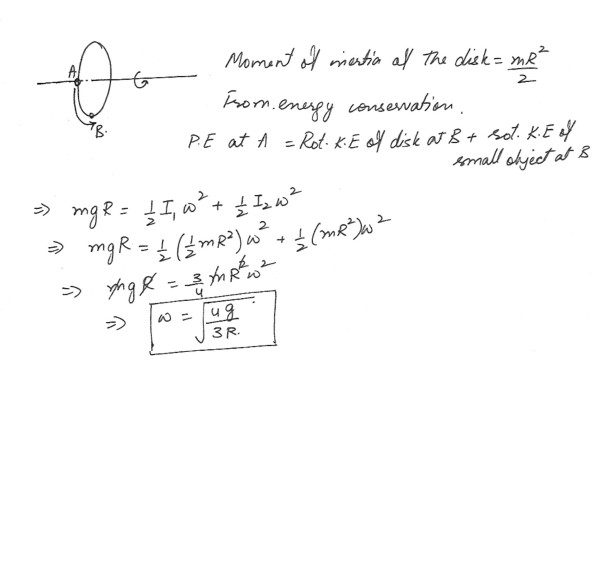
A uniform , solid disk with mass ‘m’ and ‘R’ is pivoted about a horizontal axis through its center . A small object of the same mass ‘m’ is glued to the rim of the disk .a) If the disk is released from rest with the small object at the end of a horizontal radius , find the angular speed when the small objects is directly below the axis .
Physics Rotational Mechanics Level: High School
Energy is to be stored in a flywheel in the shape of a uniform solid disk with a radius of ‘R’ and a mass of ‘m’ . To prevent structural failure of the flywheel , the maximum allowed radial acceleration of a point on its rim is ‘a’ ?a) What is the maximum kinetic energy that can be stored in the flywheel ?

