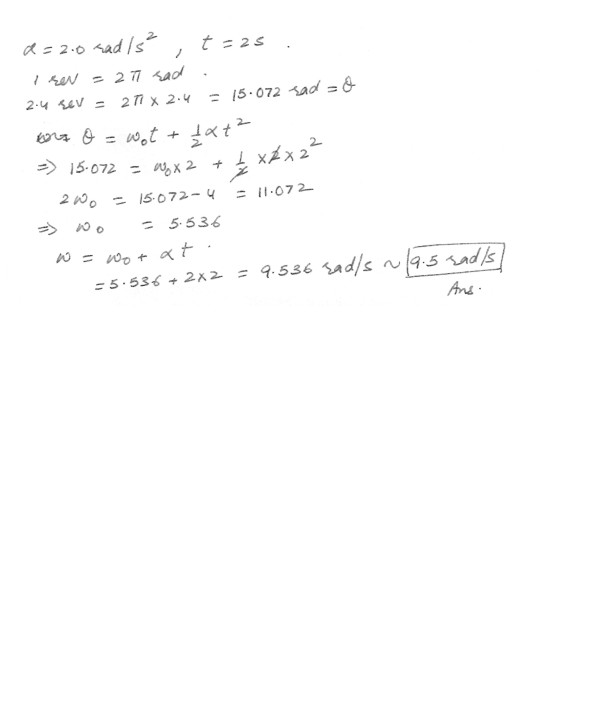Physics Rotational Mechanics Level: High School
Circular Motion
A 200 g object is moving in a circle of radius 4.0 m at a uniform speed of 6.0 m/s . What is the net force acting on the object ?a) 1.8 N away from the center of the circle
b) 1.8 N towards the center of the circle
c) 3.6 N towards the center of the circle
d) 3.6 N tangential to the circle

Physics Rotational Mechanics Level: High School
A force of 30 N is applied perpendicularly to the face of a door at a distance of 1.5 m from the hinge of the door , Find the torque on the door about its hinge .a) 2 Nm
b) 20 Nm
c) 45 Nm
d) 20 Nm
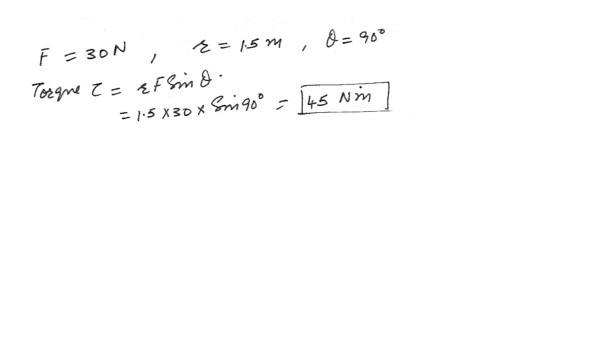
Physics Rotational Mechanics Level: High School
Find the kinetic energy of a cylindrical shaft of mass 2.0 kg and radius 10 cm rotating about its central axis at 600 rad/s .a) 1800 J
b) 18000 J
c) 1200 J
d) 12000 J
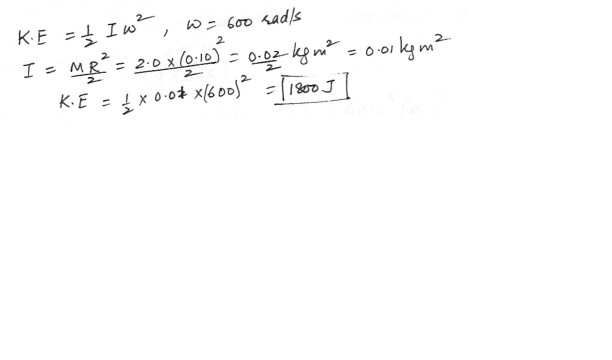
Physics Rotational Mechanics Level: High School
A pulley of mass 1.8 and radius 3.7 cm hold 2 masses : mass A = 4.6 and mass B = 5.8 kg .a) What is the rotational inertia of the pulley if it is a disk ?
b) What is the acceleration of this system if the pulley starts at rest and moves 29758.622 radians in 46 s ?
c) What is the tension in the cable holding mass A ?
d) What is the tension in the cable holding mass B ?

Physics Rotational Mechanics Level: High School
A merry-go-round of radius R = 2.0 m has a moment of inertia I = 250 kg-m2 and is rotating at 10 rev/min . A 25 kg child at rest , jumps onto the edge of the merry-go-round . What is the new angular speed of the merry-go-round ?a. 10 rev/min M
b. 8 rev/min M
c. 7 rev/min M
d. 6 rev/min M
e. 4 rev/min M

Physics Rotational Mechanics Level: High School
Starts originate as large bodies of slowly rotating gas . Because of gravity , these clumps of gas slowly decreases in size . The angular velocity of a star increases as it shrinks because ofa. Conservation of angular momentum .
b. Conservation of linear momentum.
c. Conservation of gravity .
d. The law of universal gravitation.
e. Conservation of mass .
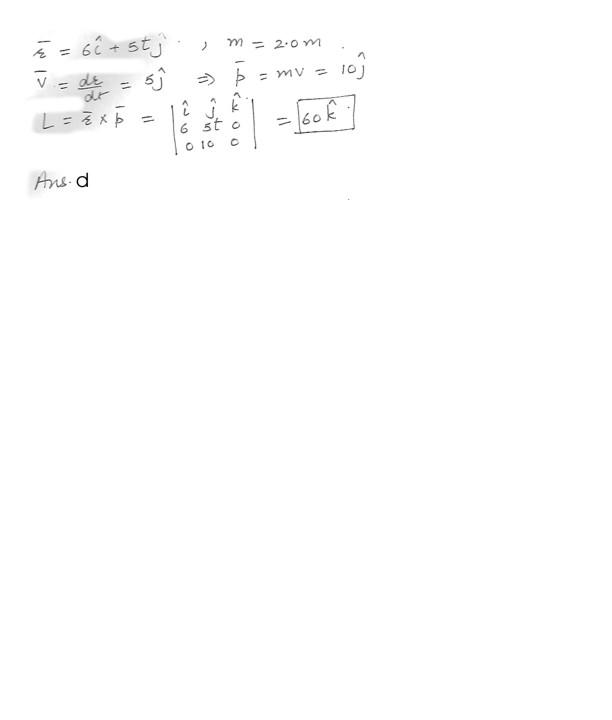
Physics Rotational Mechanics Level: High School
The position vector of a particle of mass 2.0 kg is given as a function of time by Vector r = (6.0 i + 5.0 t j) meters . What is the angular momentum of the particle (in kg-m2/s) as a function of time ?a. 60 i + 50 t 2 j .
b. 12 i + 10 tj .
c. 50 k .
d. 60 k .
e. Impossible to determine .
Physics Rotational Mechanics Level: High School
A puck of a frictionless air hockey table has a mass of 5 g and is attached to a string passing through a hole in the surface . The puck is revolving at a distance 2 meters from the hole with an angular velocity of 3 rad/s. The string is then pulled from below shortening the radius to 1 meter . The new angular velocity (in rad/s) is Diagram of a puck .1.4
2.6
3.12
4.2
5.8

Physics Rotational Mechanics Level: High School
At a certain instant the position of a stone in a sling is given by Vector r = (1.7i) meter . The linear momentum Vector of the stone is (12 j ) kg m/s . What its angular momentum Vector L = Vector r x Vector p ?a. 0
b. (20.4 k)kg m2/s
c. (20.4 j) kg m2/s
d. (20.4i) kg m2s
e. (10.0 k) kg m2/s

Physics Rotational Mechanics Level: High School
A bicycle wheel has a radius R = 32.0 cm and a mass M = 1.80 kg which you may assume to be concentrated on the outside radius . A resistive force f = 120 Newtons is applied to the rim of the tire . You are to apply a force F so that the wheel has an angular acceleration alpha = 4.50 rad/s2 . What is the strength of the applied force if the radius r of the sprocket is 4.5 centimeters ? Diagram of a bicycle wheela. 255 Newtons
b. 317 Newtons
c. 480 Newtons
d. 667 Newtons
e. 872 Newtons

Physics Rotational Mechanics Level: High School
A wheel (radius = 0.20 m) is mounted on a frictionless . horizontal axle . A light rope wrapped around the wheel supports a 0.50 kg object as shown below . When released from rest , the object falls with a downward acceleration of 5.0 m/s^2 . What is the moment of inertia of the wheel ? Diagram of a wheel .a. 0.023 kg-m2
b. 0.027 kg-m2
c. 0.016 kg-m2
d. 0.019 kg-m2
e. 0.032 kg-m2

Physics Rotational Mechanics Level: High School
A flywheel in the form of a heavy circular disk of diameter 0.600 meters and mass 200 kg is mounted on a frictionless bearing . A motor connected to the flywheel accelerates it from rest to 1000 revolution/minute . How work is done on it during this acceleration ?a. 20.2 k Joules
b. 15.3 k Joules
c. 49.3 k Joules
d. 67.3 k Joules
e. 89.7 k Joules

Physics Rotational Mechanics Level: High School
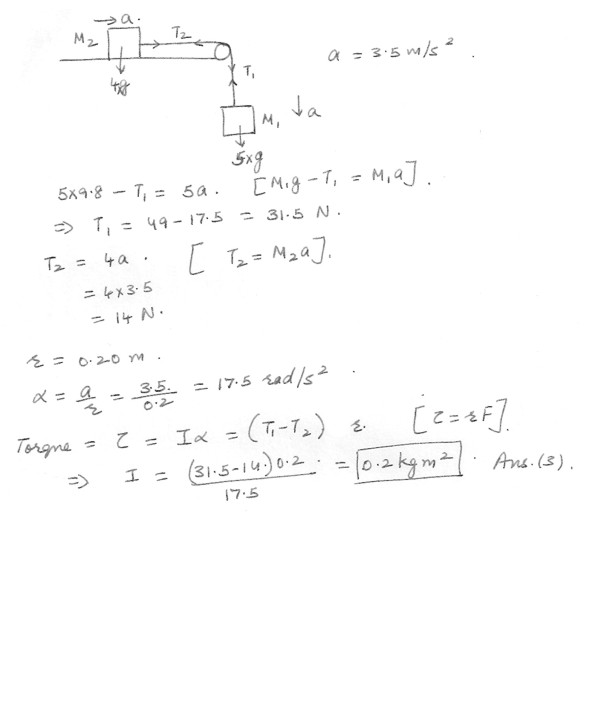
A mass (M1 = 5.0 kg ) is connected by a light rope to a mass (M2 = 4.0 kg ) which slide on smoothly . The pulley (radius = 0.20 meter ) rotates about a frictionless axle . The acceleration of M2 is 3.5 m/s2 . What is the moment of inertia of pulley ? Diagram of a mass .a. 0.29 kg-m2
b. 0.42 kg-m2
c. 0.20 kg-m2
d. 0.62 kg-m2
e. 0.60 kg-m2
Physics Rotational Mechanics Level: High School
A wheel rotates about a fixed axis with an angular velocity of 20 rad/s . During a 5.0 second time interval, the angular velocity increases to 40 rad/s. Assume that the angular acceleration was constant during the 5.0 second interval. How many revolutions does the wheel turn during through during the 5.0 second interval ?a. 20 revolutions
b. 24 revolutions
c. 32 revolutions
d. 28 revolutions
e. 39 revolutions

Physics Rotational Mechanics Level: High School
A wheel rotating about a fixed axis with a constant angular acceleration of 2.0 rad/s2. turns through 2.4 revolutions during a 2.0 seconds time interval. What was the angular velocity omega at the end of this time interval ?a. 9.5 rad/s
b. 9.7 rad/s
c. 9.3 rad/s
d. 9.1 rad/s
e. 8.8 rad/s