Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: University
Spring ForceSimple harmonic Motion
The force produced by a spring of spring constant k at displacement x can be expressed as?

Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: University
Circular Motion DynamidsFind the centripetal force of a 10-kg mass traveling at 4.0 m/s on a curve radius of 3.0 m.
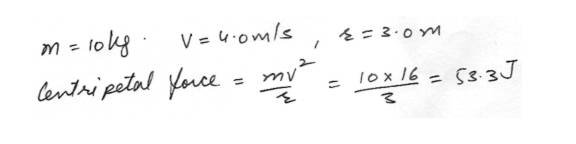
Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: University
Force in equilibriumA student has a 75g crystal hanging by a string of negligible mass from the rearview mirror in her car.
a. Determine the angle the string makes with the vertical when she accelerates at a constant rate of .35g ( maybe this is a typo and should be .35 m/s ??)
b. Determine the tension in the string during this acceleration.
c. Construct a free body diagram of the crystal
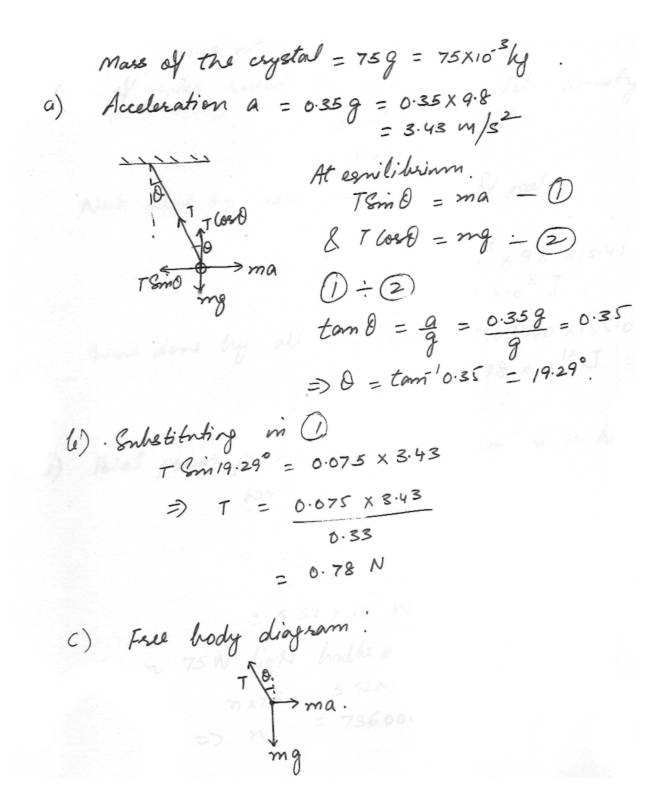
Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: University
Under GravityMartha ( a very fast cyclist) is riding her bike zalong horizontal road when she unknowingly comes to a complete drop off ( or cliff) at the end of the road. By remaining completely composed she lands perfectly on another level road exactly 121 m ahead and 18 m below and then continues on her way ( you may igore air resistance).
(a) Determine Martha s launce velocity along the original road ( upon encountering the cliff).
(b) Determine Martha s total flight time.
(c) Determine the velocity of Martha and her bike when she is exactly 12.5m below the original road.

Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: University
Motion Under GravityA cat drops from a tree limb to the ground in a perfect vacuum and is observed to reach the ground in 24.2 seconds. Upon impact the cat comes to rest without bouncing in 123 seconds.
a. Determine the velocity of the cat just prior to impact w/the ground.
b. Determine the height of the limb.
c. Determine the average acceleration of the cat during the impact (or collison
d. Using your result from part C, determine the average jerk experienced by the cat during the collision with the ground.

Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: University
Motion Under GravityA cat drops from a tree limb to the ground in a perfect vacuum and is observed to reach the ground in 24.2 seconds. Upon impact the cat comes to rest without bouncing in 123 seconds.
a. Determine the velocity of the cat just prior to impact w/the ground.
b. Determine the height of the limb.
c. Determine the average acceleration of the cat during the impact (or collison dd).
d. Using your result from part C, determine the average jerk experienced by the cat during the collision with the ground.

Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: University
Laws of MotionA skier starting at rest coasts down a slope that makes an angle of 30 degrees with the horizontal. The skier makes a vertical descent of 100m and then coasts along a level section which runs for 400 m before ending in a cliff as shown:
How large must the coefficient of friction be to just prevent the skier from going over the clifT. Assume lik is the same everywhere and neglect air resistance.( Hint treat this as a pair of I-d kinematic problems finding the skiers speed at the bottom of the hill and using this as the initial velocity on the level part.)
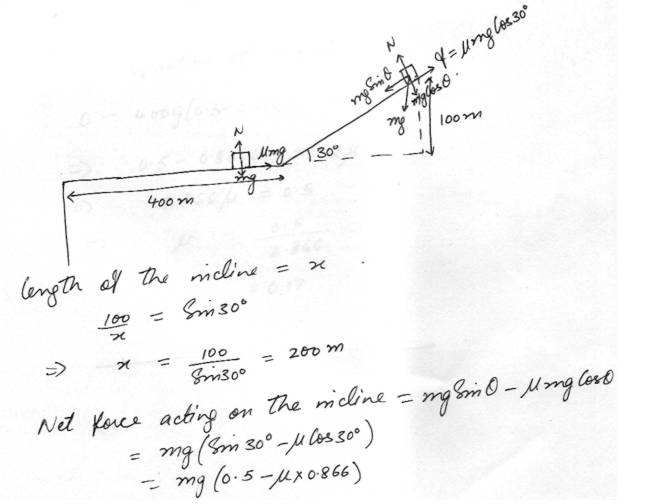
Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: University
Laws of MotionIn this problem you will discover an alternative expression of newtons 2nd Law useful for short- acting force.
a. Write the usual equation for force ( Newtons 2nd Law)
b. Write the equation defining acceleration as a rate of change :
c. What physical property is shared by both equations above?
i) a acceleration
ii) m mass
iii) F force
iv) 11 viscosity
d. Combine Equations (a) and (b) to eliminate the common variable. Then multiply both sides by change in t.
e. Check your result using dimensional analysis_ do the units on one side equal the units on the other? (recall that 1 newton = 1 kg. m/ sec2)
f. Briefly discuss the meaning of Equation (d) in the real world. (As an example the equation change in V= a times change in t means that applying an acceleration over a time interval causes a change in velocity in the same direction as the acceleration.)
g. The vector mv has a special name: momentum. re-state your interpretation of Equation using this word and the idea that m change in v is a change in momentum.
h. draw a free- body diagram and use equation (d) to explain why a magician performing the trick of pulling a tablecloth out from under a set of dishes must pull quickly ( rather than slowly ) and prefers a silky tablecloth t a sticky one.

Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: University
Laws of MotionWhich of the following is not true of a balanced at woods machine?
a. The masses can move
b. The masses must move
c. The masses can be at rest
d. A gnat landing on one of the masses will cause it to slowly sink.
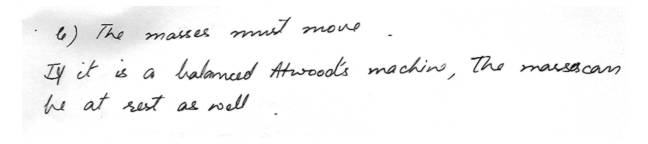
Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: University
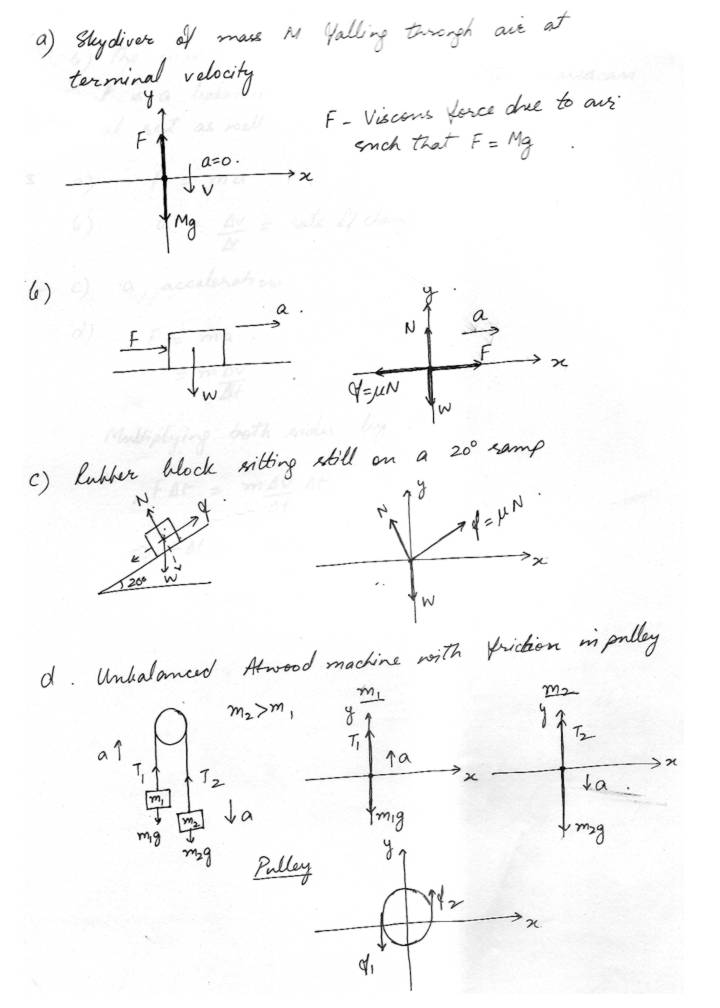
Laws of MotionDraw free - body diagrams for each of the following systems. No need to solve anything but show your choice of coordinates and label all force important to the motion. ( or lack of motion). Express friction forces in terms of the appropriate J1.
a. Skydiver of mass M. falling through air at terminal velocity.
b. Box that weighs W newtons being pushed horizontally along a rough floor.
Example: Frictionless pendulum with mass m, hanging go left of vertical.
c. Rubber block sitting still on a 20 percent ramp
d. Unbalanced Atwood machine with friction in pulley.
Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: University
ForceThe height of water at two identical dams is the same but dam A holds back a lake containing 2 km^3 of water whereas dam B holds back a lake containing 1 km^3 of water. What is the ratio of the total force on damA to that exerted on dam B? ( I took a look at this one and think it has to do with finding the mass first)

Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: University
Relative VelocitySuppose a person riding on top of a freight car shines a searchlight beam in the direction in which the train is traveling. Compare the speed of the light beam relative to the ground when a) The train is at rest. b) the train is moving. How does the behavior of the light beam differ from the behaviour of a bullet fired in the same direction from the top of the freight car?

Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: University
Projectile MotionA projectile is launched upward at an angle. What should this angle be with respect to the horizontal in order for the projectile to travel the farthest distance? explain Why?

Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: University
Equation of MotionAn experimental rocket car starting form reaches a speed of 560 km/h after a straight 400m run on the salt flat. Assuming that acceleration is constant. What was the time of the run ? What is the magnitude of the acceleration?

Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: University
Equation of motionThe driver of a pickup truck ( hay its oklahoma ) going 100 km/h applies the brakes giving the truck a uniform deceleration of 6.5m/s^2 while it travels 20.0m. What is the speed of the truck in kilometers per hour at the end of this distance? How much time has elapsed?

