Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: University
Conservation of EnergyA 12.1 gram bullet is fired horizontally into a 24.0 cm thick wooden fence post at a point 155 cm above the ground with a speed of 430 m/s. The bullet then exits the post striking the ground 3509 cm from the base of the post. Determine the average resisting force exerted by the post on the bullet.
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: University
Energy conservationSpring- Heel Jack was a legendary English criminal who was never captured because of his ability ti jump over high walls and other obstacles which his pursuers were unable to scale. It is believed that he had a powerfull spring attached to each shoe for this purpose. Find the spring constant. How far would . The spring need to be compressed in order to launch a person of some mass and some height into the air. Determine the power and energy.

Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: University
Energy conservationAn electric motor raises two packages from the floor to a platform 3.0 meters above the floor. Both packages have the same mass. The first is pulled up a frictionless inclined plane at a constant speed of 20 cm per second. The second package is lifted vertically, at the same constant speed. Which package hets to the 3.0 meter platform first? Which required more energy? Calculate the power.

Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: University
A car accelerates uniformly fromn rest to a maximum speed of 27 m/sec in a time of 30 seconds. Each wheel has a radius of 36 m and a mass of 20 kg. Calculate the angular momentum of each wheel the angular acceleration of the wheels ( alpha) and the angular velocity (omega).
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: University
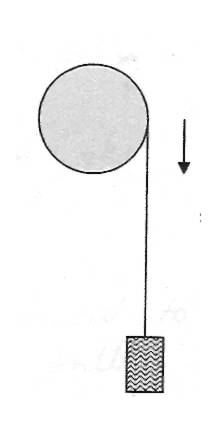
Rotational MotionA 4.0 kg mass is attached to a string that is around a pulley of the same mass as shown in the figure. The mass has gained a speed of 3.0 m/s after being released from rest and descending a distance h. The pulleys angular velocity is 40.0 rad/s. The string does not slip on the pully and there is no friction at the axle of the pulley. Calculate the tension and the Radius of the cylinder.
Question Diagram

Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: University
Laws of Motion
Water emerges from a fire hose at a a speed of 20m/s and a rate of flow of 50 L/s.
(a) Find the force with which the nozzle must be held.
(b) Find the required power of the pump motor, assuming 50 persent overall efficieiency

Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: University
Energy conservationAn electric motor raises two packages from the floor to a platform 3.0 meters above the floor. Both packages have the same mass. The first is pulled up a frictionless inclined plane at a constant speed of 20 cm per second . The second package is lifted vertically, at the same constant speed. Which package gets to the 3.0 meter platform first? Which required more energy? Calculate the power .

Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: University
Rotational MotionA 4.0 kg mass is attached to a string that is wound around a pulley of the same mass as shown in the figure. The mass has gained a speed of 3.0m/s after being released from rest and descending a distance h. The pulleys angular velocity is 40.0 rad/s. The string does not slip on the pulley and there is no friction at the axle of the pulley. Calculate the tension and the Radius of the cylinder.
Question Diagram
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: University
Spring forceA spring required a force of 1.oN to compress it 0.1m. How much work is required to stretch the spring to 0.4m?
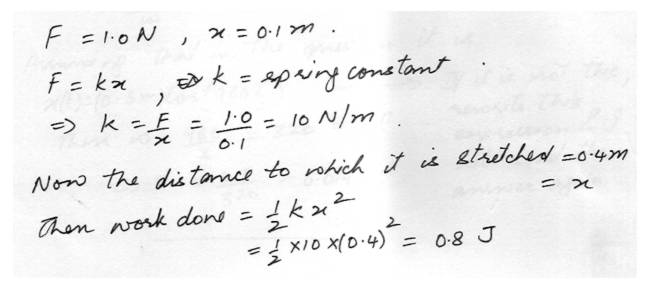
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: University
Conservation of momentumA 0.50-kg bomb is sliding along an icy pond (frictionless surface) with a velocity of 2.0m/s to the west
The bomb explodes into two pieces. After the explosion a 0.20 kg piece moves south at 4.0 m/s
What are the components of the velocity of the 0.30 kg piece?

Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: University
CollisionA 3.0-kg cart moving to the right with a speed of 1.0 m/s has a head on collision with a 5.0-kg cart that is initially moving to the left with a speed of 2 m/s. After the collision 3.0-kg cart is moving to the left with a speed of 1 m/s. What is the final velocity of the 5.0-kg cart?

Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: University
CollisionTwo pbjects of equal mass traveling toward each other with equal speeds undergo a head on collision wich one of the following statements is necessarily true?
They will exchange velocities
Their velocities will be reduced
Their velocities will be unchanged
Their velocities will be zero
Their velocities may be zero
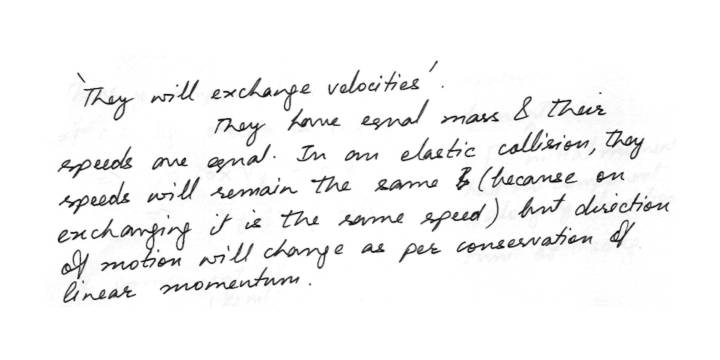
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: University
Kinetic EnergyWhich one has the largest kinetic energy?
a rain drop
a woman swimming
a jet airplane flying at maximum speed the earth moving in its orbit around the sum the space shuttle orbiting earth

Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: University
Conservation of energyWhat is the speed of a 3.31 keV electron?

Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: University
Determine the ratio of the speed of the electron to the speed of the proton at the end of their respective trajectories.

