Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: University
Spring forceA 1.5 kg block at rest on a tabletop is attached to a horizontal spring having constant 19.6 N/m. the spring is initially unstretched constant 20.ON horizontal force is applied to the object causing the string to stretch. (A) determine the speed of the block after it has moved 0.03m from equilibrium if the surface between the block and tabletop friction between block and tabletop is 0.200.

Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: University
 Conservation of momentum
Conservation of momentumAn object initially at rest breaks into two pieces as the result of an explosion. One piece (m^2) has four times the kinetic energy of the other piece (m1). What is the ratio of the masses of the two pieces?
m1/m2=
Which piece has the larger mass?
The masses must be equal.
The piece with the larger kinetic energy.
The piece with the smaller kinetic energy.

Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: University
Conservation of momentumTwo ice skaters stand at rest in the center of an ice rink. When they push off against one another the 45 kg skater acquires a speed of 0.72m/s. If the speed of the other skater is 0.84 m/s. What is this skater s mass?

Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
Conservation of energy
A snowboarder coasts on a smooth track that rises from one level to another , If the snowboarder’s initial speed is 4 m/s , the snowboarder just makes it to the upper level and comes to rest . With a slightly greater initial speed of 5 m/s , the snowboarder is still moving to the right on the upper level . what is the snowboarder’s final speed in this case ?
a) 1 m/s
b) 2 m/s
c) 3 m/s
d) 4 m/s
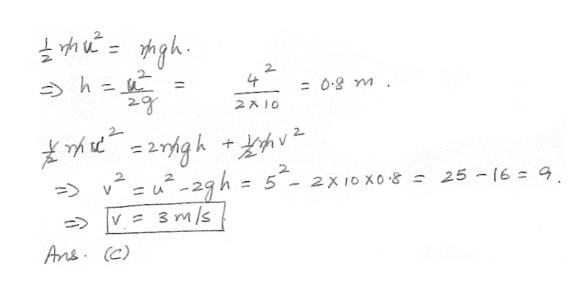
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
Conservation of energy
What should the height of a slide in a park be so that a child will reach the bottom of the slide with a speed of 15.0 m/s ? Use g = 10.0 m/s squared .
a) 22.5 m
b) 15.1 m
c) 11.3 m
d) 10.5 m
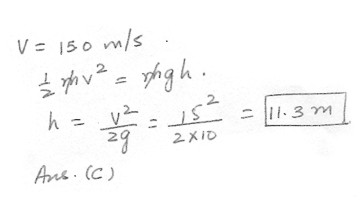
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
The ratio of the potential energy to the kinetic energy of an object of mass m at a height of 40 m above ground level is 2:1 . What is the speed of the object at that point ? Use g = 10 m/s squared .a) 10 m/s
b) 20 m/s
c) 30 m/s
d) 40 m/s
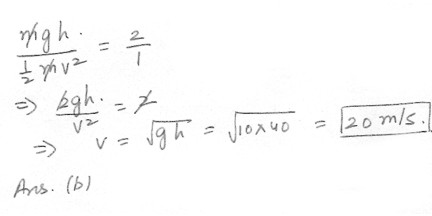
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
Conservation of energy
A mass of 1.0 kg is pushed against a spring with a spring constant of 25 N/m . As a result , the spring is compressed by 20 cm . The mass is then released .What is the amount of potential energy acquired by the spring when it is compressed ?
a) 5.0 J
b) 0.20 J
c) 0.50 J
d) 10 J
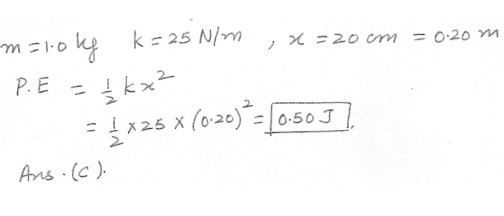
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
An object of mass 20 kg is raised vertically through a distance of 8.0 m above ground level . Using g = 10 m/s squared what is the potential energy of this object at this position ?a) 160 N/m
b) 160 Nm
c) 1600 N/m
d) 1600 Nm
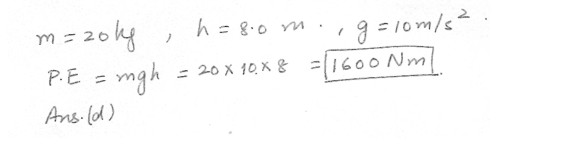
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: Middle School
An object of mass 4.0 kg is moved from a point A to a point C as follows : 0.80 m vertically from A to B , and then 0.60 m horizontally from B to C . What is the amount of work done as the object is moved from point A to C ? Use g = 10 m/s squared .a) 1.3 J form A to B and 16 J from B to C .
b) 2.2 J from A to B and 32 J from B to C .
c) 32 J from A to B and 0 J from B to C .
d) 4.0 J from A to B and 16 J from B to C .
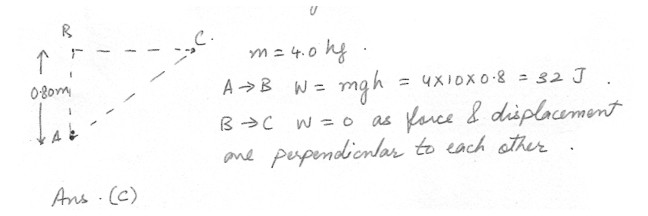
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
conservation of energy
A 4.0 bullet traveling at speed of 380 m/s enters a tree and exits the other side with a speed of 180 m/g . What was the energy transferred ?
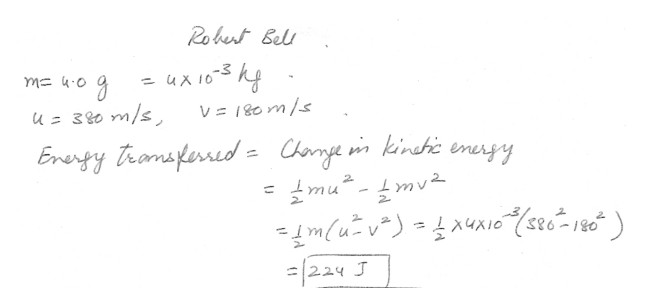
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
A 3.30 kg object is hanging from the end of a vertical spring . The spring constant is 58.0 N/m . The object is pulled 0.200 m downward and released from rest . Complete the table at “click here” . Calculate the transactional kinetic energy , the gravitational potential energy , the elastic potential energy , the total mechanical energy E for each of the vertical position indicated . The vertical positions h indicate distances above the point of release , where h = 0 ,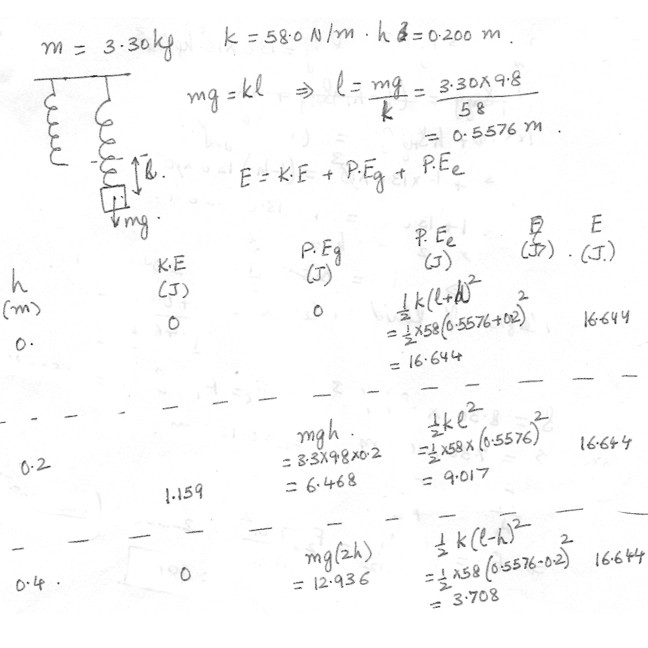
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
A single conservative force acting on a particle varies as F = (-Ax + Bx^2) i N , where A and B are constants and x is in meters .a) Calculate the potential-energy function U(x) associated with this force , taking U = 0 at x = 0 .
b) Find the change in potential energy and the change in kinetic energy as the particle moves from x = 2.00 m and x = 3.00 m .

Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
A 70.0 kg diver steps off a 10.0-m tower and drops straight down into the water. If he comes to rest 5.00 m beneath the surface of the water , determine the average resistance force exerted by the water on the diver .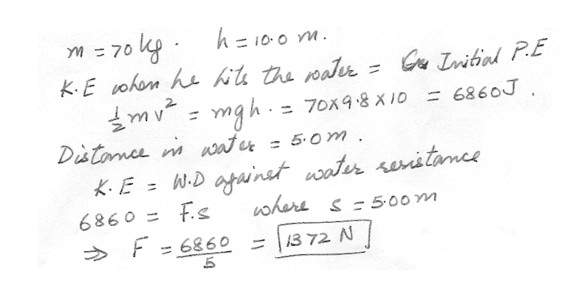
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
A 70.0 kg diver steps off a 10.0-m tower and drops straight down into the water. If he comes to rest 5.00 m beneath the surface of the water , determine the average resistance force exerted by the water on the diver .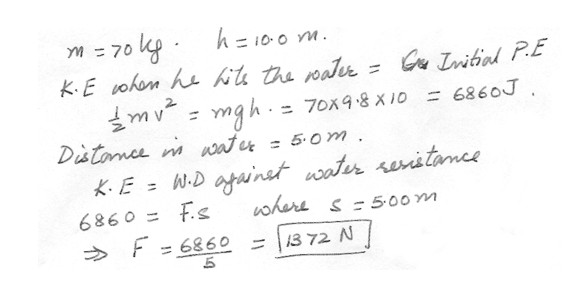
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
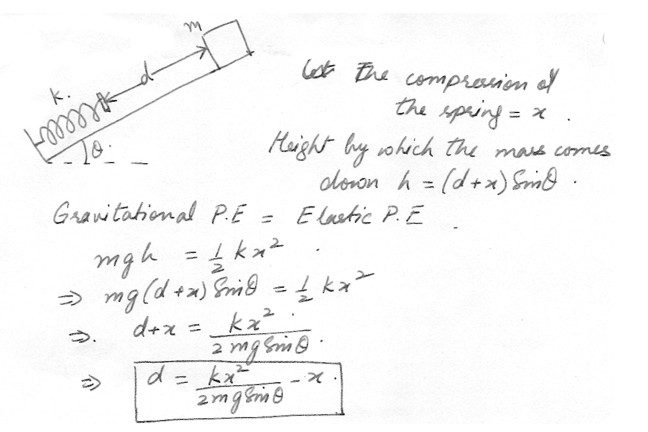
An object of mass m starts from rest and slides a distance d down a frictionless incline of angle theta . While sliding , it contacts an unstressed spring of negligible mass as shown in the figure at "click here". The object slides an additional distance x as it is brought momentarily to rest by compression of the spring (of force constant k ) . Find the initial separation d between object and the spring .