Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
In the 1950's, an experimental train that had a mass of 23800 kg was powered across a level track by a jet engine that produced a thrust of 584000 N for a distance of 557 m. Find the work done on the train . Answer in units of J. Find the change in kinetic energy. Answer in units of J. Find the final kinetic energy of the train if it started from rest. Answer in units of J. Find the final seed of the train assuming no friction
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
Inelastic Collision
A cart of mass m = 0.20 kg moving at velocity v = 3.0 m/s collides inelastically with an initially stationary cart of mass 0.40 kg . If the carts stick together , what is their combined velocity immediately after the collision ?
In the absence of frictional forces , draw a diagram labeling the force acting on each cart at the moment of collision . Are these internal or external forces ?
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
Conservation of Energy
An air cart of mass m = 0.25 kg starts moving at velocity vo = 4.0 m/s on air track . After traveling a distance of 60.0 cm, the velocity of the cart drops to v = 3.8 m/s .By how much has the kinetic energy of the cart decreased ? What is the work done by friction ? What is the magnitude of the frictional force ? Calculate the coefficient of kinetic friction between the cart and the track ?
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
Conservation of Energy
In the figure which is shown at “click here” , the pulley has negligible mass, and both it and the inclined plane are frictionless . Block A has a mass of 1.0 kg , block B has a mass of 2.0 kg , and angle theta is 30 degrees . If the blocks are released from rest with the connecting cord taut , what is their total kinetic energy when block B has fallen 25 cm ?
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
Conservation of Energy
In the figure which is shown at “click here” a block of mass m = 2 kg slides head on into a spring constant k = 320 N/m . When the block stops , it has compressed the spring by 7.5 cm . the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the floor is 0.25 . While the block is in contact with the spring and being brought to rest , what area) the work done by the spring force ?
b) the increase in thermal energy of the block-floor system ?
c) What is the blocks speed ?

Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
Conservation of Energy
A child whose weight is 267 N slides down a 6.1 m playground slides that makes an angle of 20 degree with the horizontal . The coefficient of kinetic friction between slide is 0.10 .a) How much energy is transferred to thermal energy ?
b) If she starts at the top with a speed of 00.457 m/s , what is her speed at the bottom ?

Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
Conservation of Energy
In the figure which is shown at “click here” an 8.0 kg stone rest on a spring . The spring is compressed 10.0 cm by the stone .a) What is the spring constant ?
b) The stone is pushed down an additional 30.0 cm and released . What is the elastic potential energy of the compressed spring just before that release ?
c) What is the change in the gravitational potential energy of the stone-earth system when the stone moves from the release point to its maximum height ?
d) What is that maximum height ,measured from the release point ?
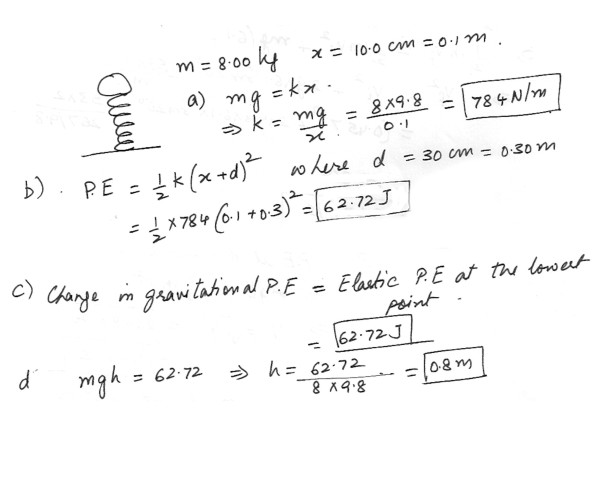
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
Vertical Circle
The string in the figure which is shown at “click here” is L = 120 cm long , has a ball attached to one end , and is fixed at its other end . the distance d from the fixed end to a fixed peg at point P is 75.0 cm . When the initially stationary ball is released with the string horizontal as shown , it will swing along the dashed arc . What is its speed whena) it reaches its lowest point ?
b) its highest point after the string catches on the peg ?

Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
Conservation of Energy
A 1.5 kg block is attached to a spring with constant 2000 N/m . The spring is then stretched a distance of .3cm and the block is released from rest . The speed of the block is it passes through the equilibrium position with no friction is 11 m/s . What is the speed of the block as it passes through the equilibrium position if a constant frictional force of 2N , and what would the strength of the frictional force be it the block reached the equilibrium position the first time when zero velocity .
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
Inelastic Collision
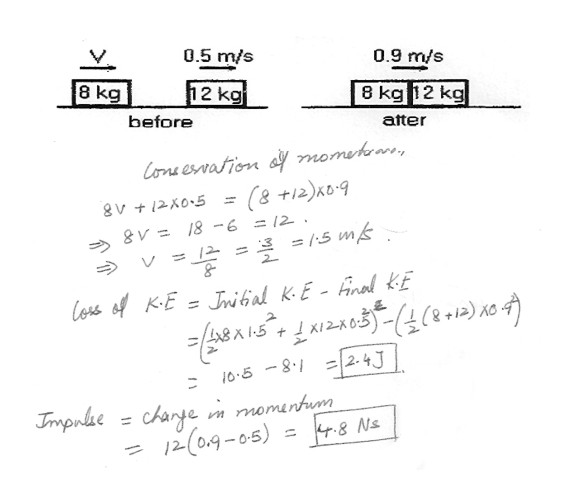
An 8 kg block has a speed v and is behind a 12 kg block that has a speed of 0.5 –m/s. The surface is frictionless . The blocks collide and couple . After the collision, the blocks have a common speed of 0.9 m/s . In the figure which is shown at “click here” , the loss of kinetic energy of the blocks due to the collision is closest to :a) 1.5 J
b) 1.8 J
c) 2.1 J
d) 2.4 J
e) 2.7 J
In the figure , the impulse on the 12 kg block due to the collision is closest to :a) 3.6 N.s
b) 4.8 N.s
c) 6.0 N.s
d) 7.2 N.s
e) 8.4 N.s
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
Elastic Collision
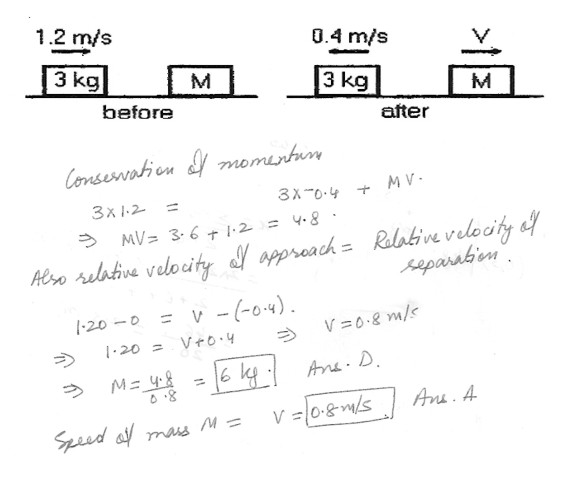
A 3.0 kg block, moving on as frictionless surface with a speed of 1.2 m/s , makes a perfectly elastic collision with a block of mass M at rest . After the collision, the 3.0 kg block recoils with a speed of 0.4 m/s . In the figure which is shown at “click here” , the mass M is closest to :a) 1.5 kg
b) 3.0 kg
c) 4.5 kg
d) 6.0 kg
e) 7.5 kg
In the figure , the speed of the block of mass M after the collision is closest to :a) 0.8 m/s
b) 1.0m/s
c) 1.2m/s
d) 1.4 m/s
e) 1.6 m/s
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
Conservation of Energy
A 0.50 kg block is held in place against the spring by a 36 N horizontal external force . The external force is removed , and the block is projected with a velocity V1 = 1.2 m/s upon separation from the spring . The block descends a ramp and has a velocity V2 = 1.8 m/s at the bottom . The track is frictionless between points A and B . The track is frictionless between points A and B . The block enters a rough section at B ,extending to E . The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.30 . The velocity of the block is v3 = 1.4 m/sat C . The block moves on to D , where it stops . In the figure at “click here” , the work done by friction between points B and C is closest to :a) -0.32 J
b) -0.40 J
c) -0.48 J
d) -0.56 J
e) -0.64 J
In the figure , the distance that the block travels between points Band D is closer to:a) 0.25 m
b) 0.35 m
c) 0.45 m
d) 0.55 m
e) 0.65 m

Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
Conservation of Energy
Two objects, one of mass m and the other of mass 2 m, are dropped from the top of a building . When they hit the ground :a) Both will have the same kinetic energy .
b) The heavier one will twice the kinetic energy of the lighter one .
c) The heavier one will have four times the kinetic energy of the lighter one .
d) The heavier one will have half the kinetic energy of the lighter one .
e) The heavier one will have one-fourth the kinetic energy of the lighter one .
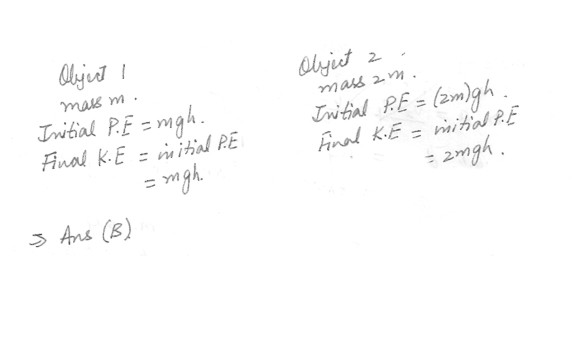
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
Vertical Circle
A 1.5 m mass less rod is loosely pinned to a frictionless pivot at 0.A 3.0 ball is attached to the other end of rod . The ball is held at A , where the rod makes 30 degrees angle above the horizontal , and is released . The ball-rod assembly then swings freely in a vertical circle between A and B . In figure which is shown at “click here” , the ball passes through C , where the rod makes an angle of 30 degree below the horizontal . The speed of the ball as it passes through C is closet to :a) 3.8 m/s
b) 4.7 m/s
c) 5.4 m/s
d) 6.1 m/s
e) 6.6 m/s
In the figure , the tension in the rod when the ball passes through the lowest point at D is closet to :a) 30 N
b) 60 N
c) 90 N
d) 120 N
e) 150 N

Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
Conservation of Energy
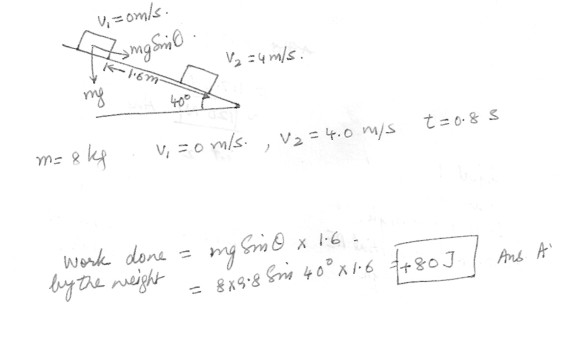
An 8.0 kg block is released from rest, v1 = 0 m/s, on a rough incline . The block moves a distance of 1.6 m down the incline , in a time interval of 0.80 s , and acquires a velocity of v2 = 4.0 m/s . In the figure which is shown at “click here”, the work done by the weight is closed to :a) +80]
1b) +100]
c) +120]
d) -80]
e) -100]