Physics Electrostatics Level: University
PotentialPoint chargess +4.1 uC and -2.2uC are placed on the x axis at (11m,0) and (-11,0) respectively. (a) sketch the electric potential on the x axis for this system. (b) your sketch should show on epoint on the x axis between the two charges where the potential vanishes. Is the point closer to the + 4.1uC charge or closer to the -2.2uC explain. (c) find the point refered to in part b

Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: University
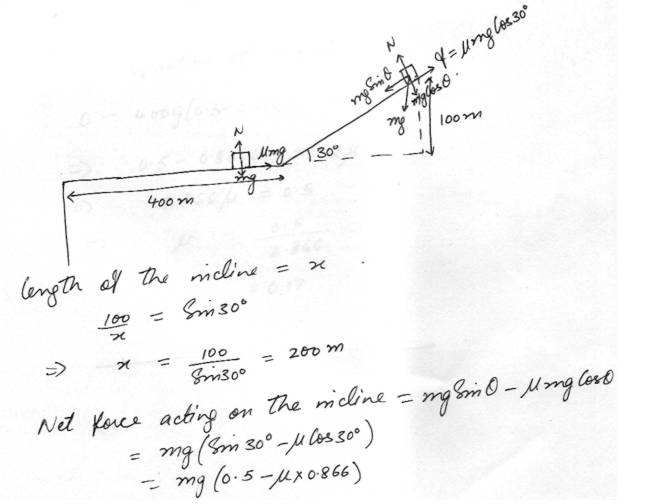
Laws of MotionA skier starting at rest coasts down a slope that makes an angle of 30 degrees with the horizontal. The skier makes a vertical descent of 100m and then coasts along a level section which runs for 400 m before ending in a cliff as shown:
How large must the coefficient of friction be to just prevent the skier from going over the clifT. Assume lik is the same everywhere and neglect air resistance.( Hint treat this as a pair of I-d kinematic problems finding the skiers speed at the bottom of the hill and using this as the initial velocity on the level part.)
Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: University
Laws of MotionIn this problem you will discover an alternative expression of newtons 2nd Law useful for short- acting force.
a. Write the usual equation for force ( Newtons 2nd Law)
b. Write the equation defining acceleration as a rate of change :
c. What physical property is shared by both equations above?
i) a acceleration
ii) m mass
iii) F force
iv) 11 viscosity
d. Combine Equations (a) and (b) to eliminate the common variable. Then multiply both sides by change in t.
e. Check your result using dimensional analysis_ do the units on one side equal the units on the other? (recall that 1 newton = 1 kg. m/ sec2)
f. Briefly discuss the meaning of Equation (d) in the real world. (As an example the equation change in V= a times change in t means that applying an acceleration over a time interval causes a change in velocity in the same direction as the acceleration.)
g. The vector mv has a special name: momentum. re-state your interpretation of Equation using this word and the idea that m change in v is a change in momentum.
h. draw a free- body diagram and use equation (d) to explain why a magician performing the trick of pulling a tablecloth out from under a set of dishes must pull quickly ( rather than slowly ) and prefers a silky tablecloth t a sticky one.

Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: University
Laws of MotionWhich of the following is not true of a balanced at woods machine?
a. The masses can move
b. The masses must move
c. The masses can be at rest
d. A gnat landing on one of the masses will cause it to slowly sink.
Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: University
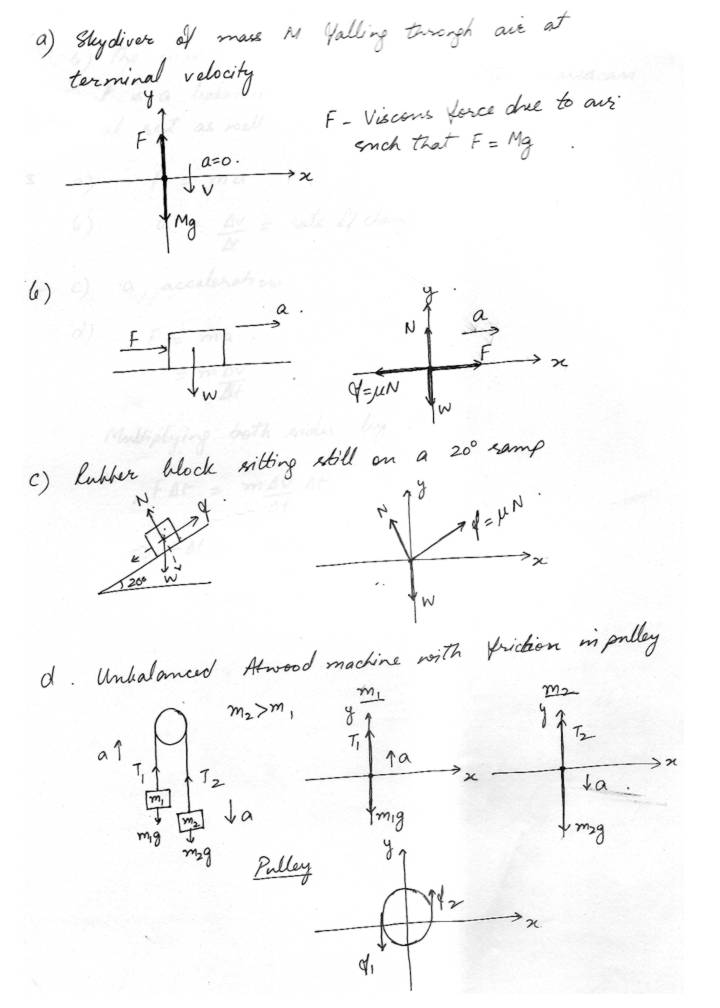
Laws of MotionDraw free - body diagrams for each of the following systems. No need to solve anything but show your choice of coordinates and label all force important to the motion. ( or lack of motion). Express friction forces in terms of the appropriate J1.
a. Skydiver of mass M. falling through air at terminal velocity.
b. Box that weighs W newtons being pushed horizontally along a rough floor.
Example: Frictionless pendulum with mass m, hanging go left of vertical.
c. Rubber block sitting still on a 20 percent ramp
d. Unbalanced Atwood machine with friction in pulley.
Physics Rotational Mechanics Level: University
Center of MassA uniform thin machine part is a flat circular plate of radius 2R that has a circular hole of radius R cut out of it. The centre of the hole is a distance 0.8 R from the centre of the plate. What is the position of the centre of mass of the plate (Think of a solid plate as being the sun of the given plate plus a small one of radius R)

Physics Rotational Mechanics Level: University
TorqueAssume a cyclist of weight mg can exert a force on the pedals equal to 0.9 mg on the avereage. Assume the mass of the bike is 12 kg and that of the rider is 60 kg . If the pedals rotate in a circle of radius 18 cm/the wheels have a radius of 34 cm, and the front and back sprockets on which the chain runs have 42 and 19 teeth respectively determine the maximum steepness of hill the cyclist can climb at constant speed. Ignore friction. Assum the cyclistss avg force is always a) downard b ) tangential to pedal motion.

Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: University
Energy conservationSpring- Heel Jack was a legendary English criminal who was never captured because of his ability ti jump over high walls and other obstacles which his pursuers were unable to scale. It is believed that he had a powerfull spring attached to each shoe for this purpose. Find the spring constant. How far would . The spring need to be compressed in order to launch a person of some mass and some height into the air. Determine the power and energy.

Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: University
Energy conservationAn electric motor raises two packages from the floor to a platform 3.0 meters above the floor. Both packages have the same mass. The first is pulled up a frictionless inclined plane at a constant speed of 20 cm per second. The second package is lifted vertically, at the same constant speed. Which package hets to the 3.0 meter platform first? Which required more energy? Calculate the power.

Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: University
A car accelerates uniformly fromn rest to a maximum speed of 27 m/sec in a time of 30 seconds. Each wheel has a radius of 36 m and a mass of 20 kg. Calculate the angular momentum of each wheel the angular acceleration of the wheels ( alpha) and the angular velocity (omega).
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: University
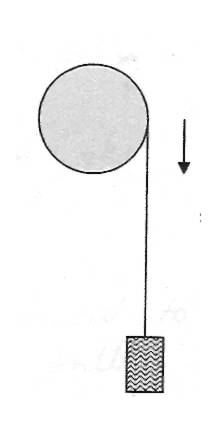
Rotational MotionA 4.0 kg mass is attached to a string that is around a pulley of the same mass as shown in the figure. The mass has gained a speed of 3.0 m/s after being released from rest and descending a distance h. The pulleys angular velocity is 40.0 rad/s. The string does not slip on the pully and there is no friction at the axle of the pulley. Calculate the tension and the Radius of the cylinder.
Question Diagram

Physics Properties Of Matter Level: University
GasA piston weiging 12 N rests on a sample of gas in a cylinder 5 cm in diameter (a) What is the gauge pressure in the gas (b) What is the absolute pressure in the gas ( in this one is it just a matter of finding the area of the circle of the cylinder which is PI 2.5 r and dividing into 12)

Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: University
ForceThe height of water at two identical dams is the same but dam A holds back a lake containing 2 km^3 of water whereas dam B holds back a lake containing 1 km^3 of water. What is the ratio of the total force on damA to that exerted on dam B? ( I took a look at this one and think it has to do with finding the mass first)

Physics Properties Of Matter Level: University
Law of floatationA design has been proposed for a modern helium-filled airship that is to have a useful lift of 5x 10^5 kg at sea level.
(a)How many m^3 of helium must the airship contain?
(b) The length of the airship would be 400m. If it were a cylinder what would its diameter be?

Physics Properties Of Matter Level: University
Archemadies PrincipleA steel tank whose capacity of 200L has a mass of 36 kg.
(a)Will it float in seawater when emtpy.
(b) When filled with fresh water.
(c)When filled with gasoline

