Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
Conservation of Energy
An air cart of mass m = 0.25 kg starts moving at velocity vo = 4.0 m/s on air track . After traveling a distance of 60.0 cm, the velocity of the cart drops to v = 3.8 m/s .By how much has the kinetic energy of the cart decreased ? What is the work done by friction ? What is the magnitude of the frictional force ? Calculate the coefficient of kinetic friction between the cart and the track ?
Physics Waves And Oscillations Level: High School
Simple Harmonic Motion
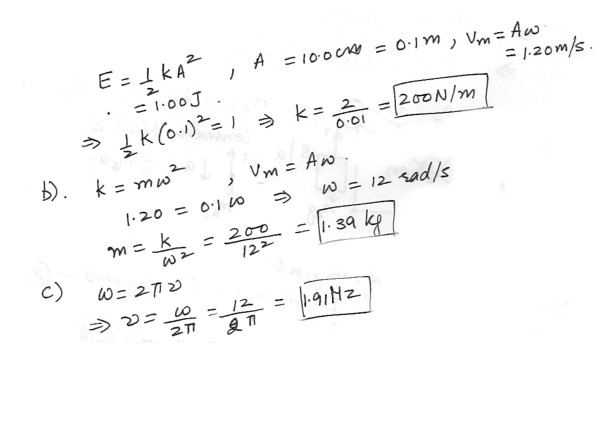
An oscillating block-spring system has a mechanical energy of 1.00 J , and amplitude of 10.0 cm , and a maximum speed of 1.20 m/s . Finda) the spring constant
b) the mass of the block
c) the frequency of the oscillation
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
Conservation of Energy
In the figure which is shown at “click here” , the pulley has negligible mass, and both it and the inclined plane are frictionless . Block A has a mass of 1.0 kg , block B has a mass of 2.0 kg , and angle theta is 30 degrees . If the blocks are released from rest with the connecting cord taut , what is their total kinetic energy when block B has fallen 25 cm ?
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
Conservation of Energy
In the figure which is shown at “click here” a block of mass m = 2 kg slides head on into a spring constant k = 320 N/m . When the block stops , it has compressed the spring by 7.5 cm . the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the floor is 0.25 . While the block is in contact with the spring and being brought to rest , what area) the work done by the spring force ?
b) the increase in thermal energy of the block-floor system ?
c) What is the blocks speed ?

Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
Conservation of Energy
A child whose weight is 267 N slides down a 6.1 m playground slides that makes an angle of 20 degree with the horizontal . The coefficient of kinetic friction between slide is 0.10 .a) How much energy is transferred to thermal energy ?
b) If she starts at the top with a speed of 00.457 m/s , what is her speed at the bottom ?

Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
Conservation of Energy
In the figure which is shown at “click here” an 8.0 kg stone rest on a spring . The spring is compressed 10.0 cm by the stone .a) What is the spring constant ?
b) The stone is pushed down an additional 30.0 cm and released . What is the elastic potential energy of the compressed spring just before that release ?
c) What is the change in the gravitational potential energy of the stone-earth system when the stone moves from the release point to its maximum height ?
d) What is that maximum height ,measured from the release point ?
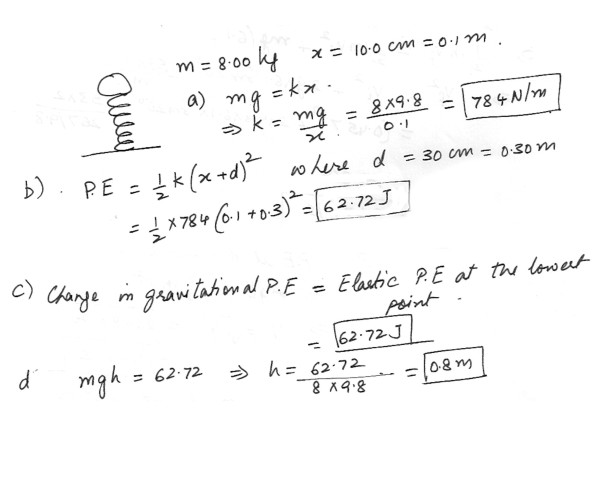
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
Vertical Circle
The string in the figure which is shown at “click here” is L = 120 cm long , has a ball attached to one end , and is fixed at its other end . the distance d from the fixed end to a fixed peg at point P is 75.0 cm . When the initially stationary ball is released with the string horizontal as shown , it will swing along the dashed arc . What is its speed whena) it reaches its lowest point ?
b) its highest point after the string catches on the peg ?

Physics Heat & Thermodynamics Level: High School
Ideal Gas Equation
a) An ideal gas occupies a volume of 2.8 cm^3 at 20 degree C and atmospheric pressure . Determine the number of molecules of gas in the container .
b) If the pressure is reduced to 2.6 x 10^-11 Pa ( an extremely good vacuum) while the temperature remains constant , how many moles of gas remain in the container ?

Physics Heat & Thermodynamics Level: High School
Thermal Expansion
A hollow aluminum cylinder 23.0 cm deep has an internal capacity of 2.00 L at 20.0 degree C . It is completely filled with turpentine and then warmed to 74.0 degree C .a) How much turpentine overflows ?
b) If it is then cooled back to 20.0 degree C , how far below the surface of the cylinder’s rim is the turpentine’s surface ?

Physics Heat & Thermodynamics Level: High School
Thermal Expansion
On a day when the temperature is 20.5 degree C , a concrete walk is poured in such a way that its ends are unable to move .a) What is the stress in the cement when its temperature is 49.5 degree C ?

Physics Heat & Thermodynamics Level: High School
Thermal Expansion
On a day when the temperature is 20.5 degree C , a concrete walk is poured in such a way that its ends are unable to move .a) What is the stress in the cement when its temperature is 49.5 degree C ?

Physics Heat & Thermodynamics Level: High School
Thermal Expansion
The average coefficient of volume expansion for carbon tetrachloride is 5.81 x 10^-4 (degree C)^-1 . If a 49.5 gal steel container is filled completely with carbon tetrachloride when the temperature is 10.0 degree C , how much will spill over when the temperature rises to 30.0 degree C ?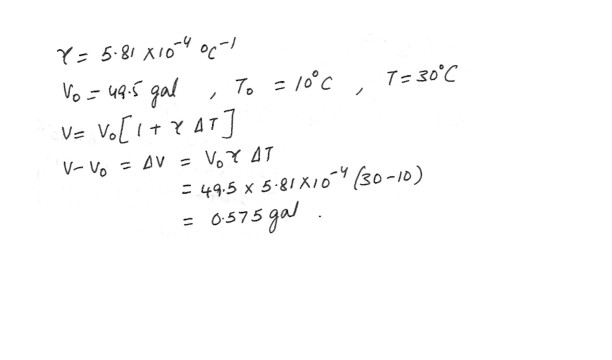
Physics Ray Optics Level: High School
Two optically flat sheets of glass of length 10 cm are in contract at one end and held separate at the one end by a hair of diameter 30 micro m , so that a thin wedge of air is formed between them . Monochromatic light of wavelength 590 nm illuminates the sheets from above by normal incidence .a) Long, straight closely-spaced interference fringes are seen . Explain why . Explain carefully whether the lone of contact between the two sheets is a bright fringe or a dark fringe .
b) Calculate the horizontal separation of the fringes .

Physics Ray Optics Level: High School
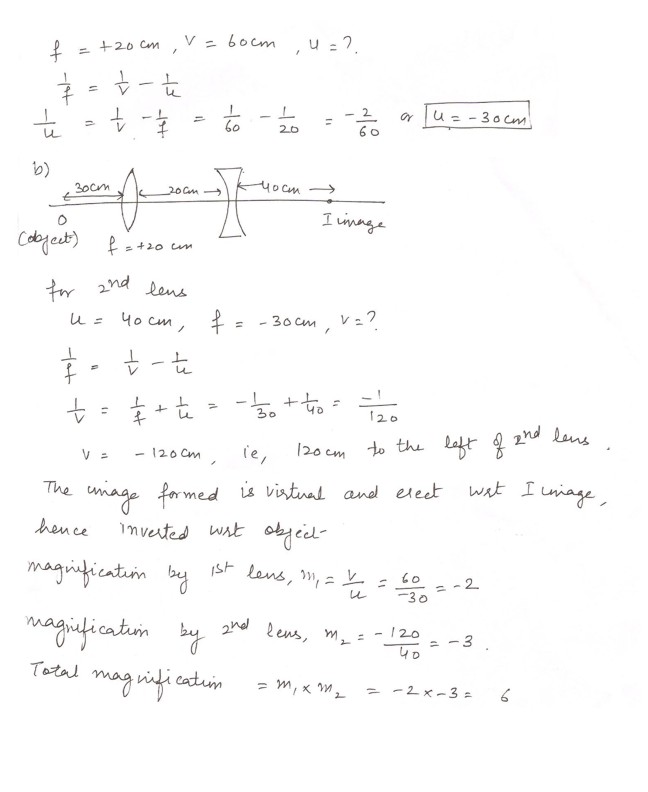
A lens of +20 cm focal length forms an inverted image 60 cm to the right of the lens. A second lens of focal length -30 cm is placed 20 cm to the right of the first lens .a) Where is the object relative to the first lens (+20 cm focal length) ?
b) Locate and fully describe the final image , including its overall magnification .
Physics Ray Optics Level: High School
a) A double convex lens , both surfaces of which have radii of 20 cm , is made of glass whose refractive index is 1.5. Find the size of the lens .
b) An object 40.0 mm high is placed 52.4 cm from a converging lens . An image is formed 25.8 cm from the lens . Find the size of the image , whether it is real or virtual and the focal length of the lens .
c) A concave spherical mirror of radius of curvature 2 m is mounted on a wall. You walk towards it at a speed of 1.5 ms^-1 . When you are at a distance of 5 m , find the location of your image and its apparent speed .

