Physics Properties Of Matter Level: High School
Equation of Continuity
A garden hose of inner radius 0.5 cm carries water at 1.2 m/s . The nozzle at the end has radius 0.21 cm . How fast does the water move through the nozzle ?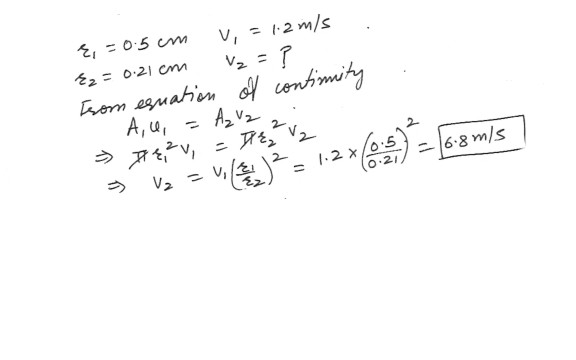
Physics Properties Of Matter Level: High School
Archimedes Principle
A cylindrical disk has volume 8.97 x 10^-3 m^3 and mass 8.16 kg . The disk is floating on the surface of some water with its flat surface horizontal . The area of each flat surface is 0.637 m^2 .a) What is the specific gravity of the disk ?
b) How far below the water level is its bottom surface ?
c) How far above the water level is its top surface ?

Physics Properties Of Matter Level: High School
Pressure
A container has a large cylindrical lower part with a long thin cylindrical neck . The lower part of the container holds 12.5 m^3 of water and the surface area of the bottom of the container is 4.76 m^2 . The height of the lower part of the container is h1 = 3.20 m and the neck contains a column of water h2 = 8.80 m high . The total volume of the column of water in the neck is 0.200 m^3 , what is the magnitude of the force exerted by the water on the bottom of the container ?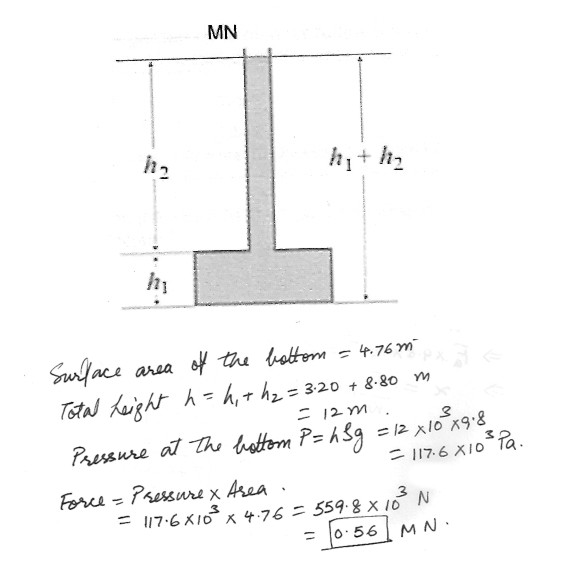
Physics Properties Of Matter Level: High School
Pressure
At the surface of a freshwater lake the pressure is 101 kPa .a) What is the pressure increase in going 34.8 m below the surface ?
b) What is the approximate pressure decrease in going 35 cm above the surface ? Air at 20 degree C has density of 1.2 kg/m^3 .

Physics Properties Of Matter Level: High School
Pascal’s Law
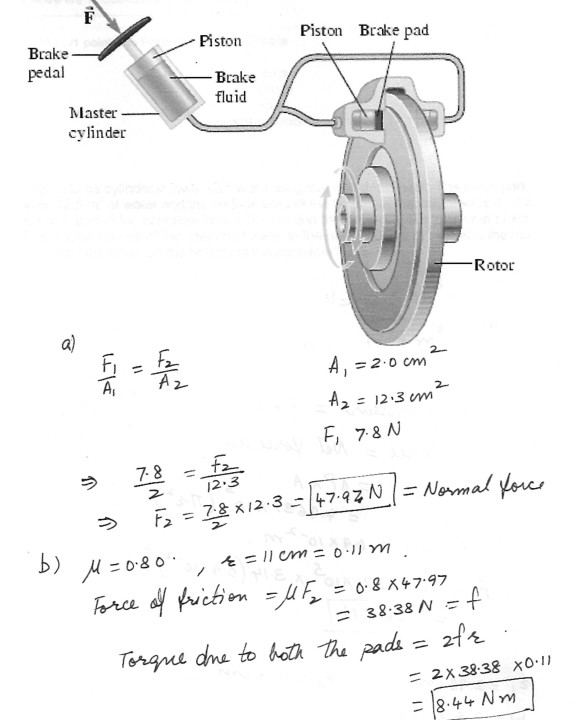
Depressing the brake pedal in a car pushes on a piston with cross-sectional area 2.0 cm^2 . The piston applies pressure to the brake fluid , which is connected to two pistons , each with area 12.3 cm^2 . Each of these pistons presses a brake pad against one side of a rotor attached to one of the rotating wheels . See the figure at “click here” .a) When the force applied by the brake pedal to the small piston is 7.8 N , what is the normal force applied to each side of the rotor ?
b) If the coefficient of kinetic friction between a brake pad and the rotor is 0.80 and each pad is (on average) 11 cm from the rotation axis of the rotor , what is the torque on the rotor due to the two pads ?
Physics Vectors Level: High School
Pascal’s Law
In a hydraulic lift , the radii of the pistons are 2.98 cm and 10.8 cm. A car weighing W = 8.5 kN is to be lifted by the force of the large piston .a) What force Fa must be applied to the small piston ?
b) When the small piston is pushed in by 9.8 cm, how far is the car lifted ?

Physics Properties Of Matter Level: High School
Pressure
The pressure inside a bottle of champagne is 4.9 atm higher than the air pressure outside . The neck of the bottle has an inner radius of 0.9 cm . What is the friction force on the cork due to the neck of the bottle ?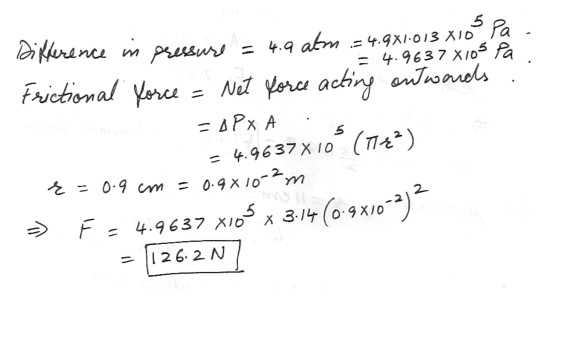
Physics Properties Of Matter Level: High School
Pressure
What is the average pressure on the soles of the feet of a standing 86.5 kg person due to the contact force with the floor ? Each foot has a surface area of 0.021 m^2 .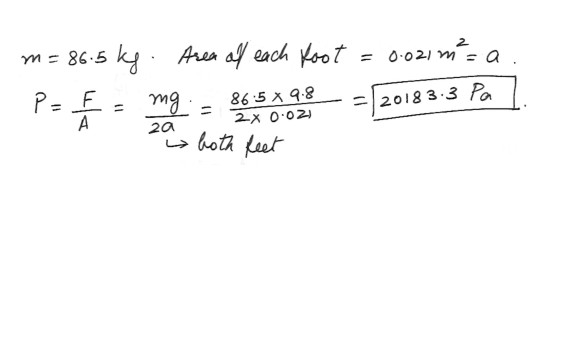
Physics Rotational Mechanics Level: High School
Conservation of Angular Momentum
Two disks are mounted (like a merry-go-round ) on low friction bearings on the same axle and can be brought together so that they couple and rotate as one unit . The first disk, with rotational inertia 3.30 kg m^2 about its central axis , is set spinning counterclockwise at 450 rev/min . They then couple togethera) What is their angular speed after coupling ? If instead the second disk is set spinning clockwise at 900 rev/min ,
b) what are their angular speed
c) the direction of rotation after they couple together ?

Physics Rotational Mechanics Level: High School
Loop The Loop
In the figure which is shown at “click here“ , a solid brass ball of mass 0.280 g will roll smoothly along a loop-the-loop track when released from rest along the straight section the circular loop has radius R = 14.0 cm , and the ball has radius r<b) magnitude and
c) direction of the horizontal force component acting on the ball at point Q ?
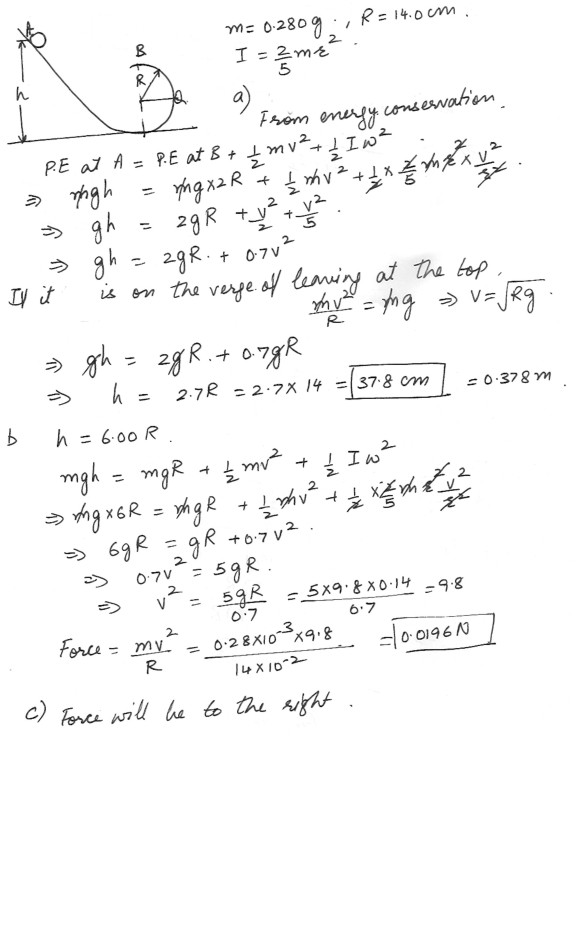
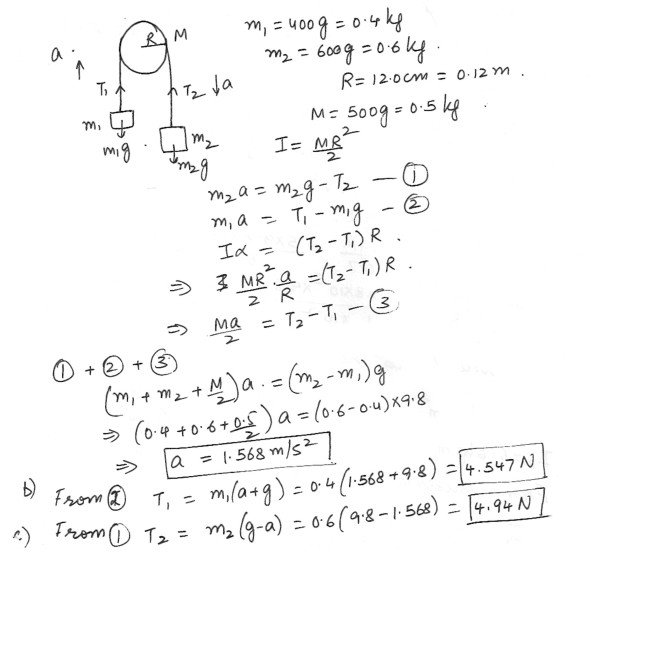
Physics Rotational Mechanics Level: High School
Pulley with rotational Inertia
In the figure which is shown at “click here” two blocks, of mass m1 = 400 g and m2 = 600 g , are connected by a massless cord that is wrapped around a uniform disk of mass M = 500 g and radius R = 12.0 cm . The disk can rotate without friction about a fixed horizontal axis through its center ; the cord cannot slip on the disk . The system is released from rest . Find .a) the magnitude of the acceleration of the blocks
b) the tension T1 in the cord at the left
c) the tension T2 iu the cord at the right
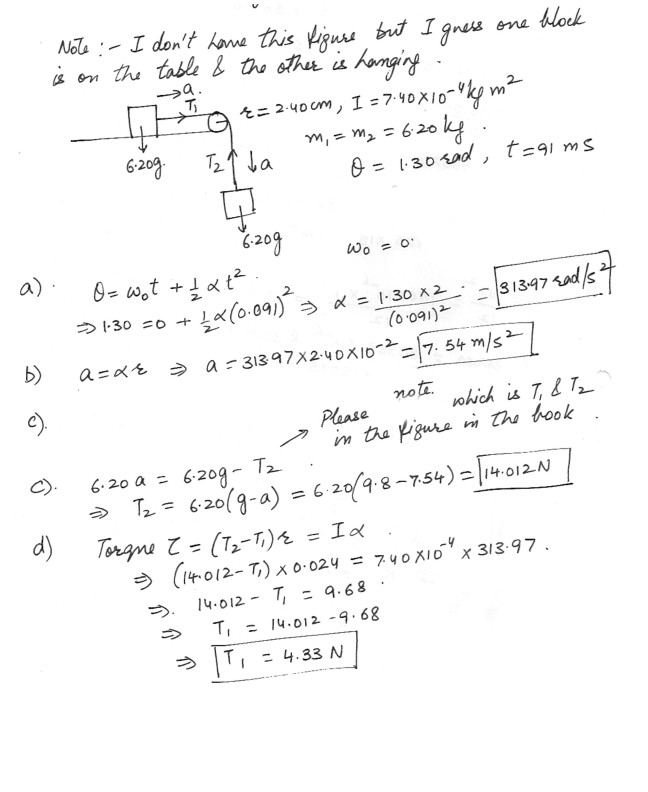
Physics Rotational Mechanics Level: High School
Pulley with rotational Inertia
In the figure which is shown at ‘click here’ two 6.20 kg blocks are connected by a massless string over a pulley of radius 2.40 cm and rotational inertia 7.40 x 10^-4 kg m^2 . the string does not slip on the pulley , it is not known whether there is friction between the table and the sliding block; the pulleys axis is frictionless. When this system is released from rest , the pulley turns through 1.30 rad in 91.0 ms and the acceleration of the block is constant . What area) the magnitude of the pulley’s angular acceleration
b) the magnitude of either blocks acceleration
c) string tension T1
d) string tension T2
Physics Rotational Mechanics Level: High School
Rotational Kinetic Energy
A thin rod of length 0.75 m and mass 0.42 kg is suspended freely form one end . It is pulled to one side and then allowed to swing like a pendulum, passing through its lowest position with angular speed 4.0 rad/s . Neglecting friction and air resistance , finda) The rod’s kinetic energy at is lowest position .
b) How far above that position the center of mass rises .

Physics Rotational Mechanics Level: High School
Moment of Inertia
Figure at “click here” shows an arrangement of 15 identical disk that have been glued together in a rod-like shape of length L = 1.0000 m and (total) mass M = 100.0 mg . the arrangement can rotate about a perpendicular axis through its central disk at point O .a) What is the rotational inertia of the arrangement about that axis ?
b) If we approximated the arrangement as being a uniform rod of mass M and length L , what percentage error would we make in using the formula in table 10-2e to calculate the rotational inertia ?

Physics Rotational Mechanics Level: High School
Circular Motion and Friction
A record turntable is rotating at 33 1/3 rev/min . A watermelon seed is on the turntable 6.0 cm from the axis of rotation .a) Calculate the acceleration of the seed , assuming that it does not slip .
b) What is the minimum value of the coefficient of static friction between the seed and the turntable if the seed is not to slip ?
c) Suppose that the turntable achieves its angular speed by starting from rest and undergoing a constant angular acceleration for 0.25 s. Calculate the minimum coefficient of static friction required for the seed not to slip during the acceleration period .

