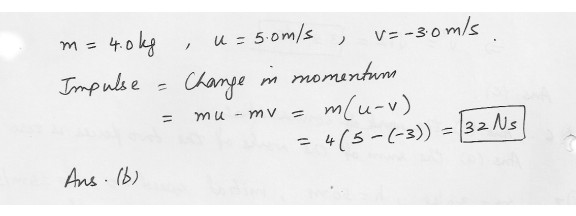Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: High School
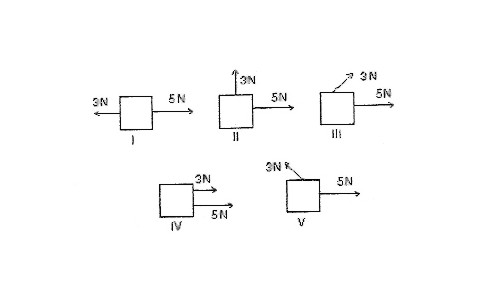
Two forces one with a magnitude of 3N and other with a magnitude of 5N, are applied to an object. For which orientations of the forces shown in the diagram is the magnitude of the acceleration of the object the least ?a) I
b) II
c) III
d) IV
e) V
Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: High School
Mass deffers from weight in that :a) all objects have weight but some lack mass
b) weight is force and mass is not
c) the mass of an object is always more than its weight
d) mass can only be expressed in the metric system.
e) there is no difference
Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: High School
The inertia of a body tends to cause the body toa) speed up
b) slow down
c) resist any change in motion
d) fall toward the earth
e) decelerate due to friction
Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: High School
The term “mass” refers to the same physical concept as:a) weight
b) inertia
c) force
d) acceleration
e) volume
Physics Kinematics Level: High School
Acceleration is always in the direction :a) of the displacement
b) of the initial velocity
c) of the final velocity.
d) of the net force.
e) opposite to the frictional force.
Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: High School
The standard 1-kg mass is attached to a compressed spring and the spring is released . If the mass initially has an acceleration of 5.6 m/s^2 , the force of the spring has a magnitude of :2.8N
b) 5.6N
c) 11.2N
d) 0
e) E. an undetermined amount.
Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: High School
A newton is the force :a) of gravity on a 1 kg body
b) of gravity on a 1 g body
c) that gives a 1g body an acceleration of 1 cm/s^2
d) that gives a 1 kg body an acceleration of 1m/s^2
e) that gives a 1 kg body an acceleration of 9.8 m/s^2
Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: High School
An example of an internal reference frame is :a) any frame that is not accelerating
b) a frame attached to a particle on which no forces act.
c) any frame that is at rest.
d) a frame attached to the centre of the universe.
e) a frame attached to the earth.
Physics Rotational Mechanics Level: High School
A 3.0 kg mass is positioned at (0,0.8) , and a 1.0 kg is positioned at (12,0). What are the coordinates of a 4.0 kg mass which will result in the centre of mass of the system of three masses being located at the origin , (0,0) ?a) (-3.0,-6.0)
b) (-12,-8.0)
c) (3.0,6.0)
d) (-6, -3)

Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
A 2.0 kg mass moving to the east at a speed of 4.0 m/s collides head-on in a perfectly inelastic collision with a stationary 2.0 kg mass . How much kinetic energy is lost during this collision ?a) 16 J
b) 4 J
c) 8 J
d) zero

Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: High School
If you know the impulse that has acted on a body of mass m you can calculate ,a) its initial velocity
b) its final velocity
c) its final momentum
d) the change in its velocity
e) the acceleration during the impulse

Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: High School
A car of mass m1 traveling at velocity V passes a car of mass m2 parked at the side of the road . The momentum of the system of the two cars area) 0
b) (m1)*V
c) (m1-m2)*V
d) (m1)*V/(m1+m2)
e) (m1+m2)*V
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
A 3.0 kg object moving 8.0 m/s in the positive x direction has a one-dimensional elastic collision with an object (mass = M) initially at rest . After the collision the object of unknown mass has a velocity of 6.0 m/s in the positive x direction . What is M ?a) 7.5 kg
b) 5.0 kg
c) 6.0 kg
d) 4.2 kg
e) 8.0 kg

Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
A 6 kg object is moving 5.0 m/s collides with and sticks to a 2.0 kg object . After the collision the composite object is moving 2.0 m/s in a direction opposite to the initial direction of motion of the 6.0 kg object . Determine the speed of the 2.0 kg object before the collision .a) 15 m/s
b) 7 m/s
c) 8 m/s
d) 23 m/s
e) 11 m/s

Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
A 4.0 kg particle is moving horizontally with a speed of 5.0 m/s when it strikes a vertical wall . The particle rebound with a speed of 3.0 m/s . what is the magnitude of the impulse delivered to the particle ?a) 24 N.s
b) 32 N.s
c) 40 N.s
d) 31 N.s
e) 8.0 N.s