Physics Heat & Thermodynamics Level: University
Kinetic theory of GasThe absolute temperature of an ideal gas is directly proportional to which of the following properties ( when taken as an average) of the molecules of that gas?
a. Speed
b. Momentum
c. Mass
d. kinetic energy
Physics Heat & Thermodynamics Level: University
In a cloud formation water vapor turns into water droplets which get bigger and bigger until it rains. This will cause the temperature of the air in the clouds to:a. Get warmer
b. Get cooler
c. Be completely unaffected
d.There is no air in clouds
Physics Heat & Thermodynamics Level: University
Transfer of heatWhich of the following processes of heat transfer may take place in a vacuum?
a. Conduction
b. Convection
c.Radiation
d. Induction
e. None of the above choices are valid
Physics Heat & Thermodynamics Level: University
A heat pump is used to heat a building. The outside temperature is - 5 C and the temperature inside the building is to be maintained at 22 C. The pump's coefficient of performance is 3.8 and the the heat pump delievers 7.54 MJ of heat to the building each hour. If the heat pump is a Carnot engine working in reverse at what rate must work be done to run the heat pump?

Physics Heat & Thermodynamics Level: University
Efficiency of engineA inventor claims to have constructed an engine that has an efficiency of 75 percent when operated between the boiling and freezing points of water. Is this possible? Explain.

Physics Heat & Thermodynamics Level: University
Specific Heat & Latent HeatFind the minimum amount of energy required to completely melt at 130 g of silver initially at 15.0 C.

Physics Heat & Thermodynamics Level: University
A steel rod is 3.000 cm in diameter at 25 C. A brass ring has an interior diameter of 2.992 cm at 25 C. At what common temperature will the ring just slide onto the rod?

Physics Heat & Thermodynamics Level: University
EntropyA 2.0 kg block of lead melts at its melting point of 327.3 C. Calculate the change in its entrophy.
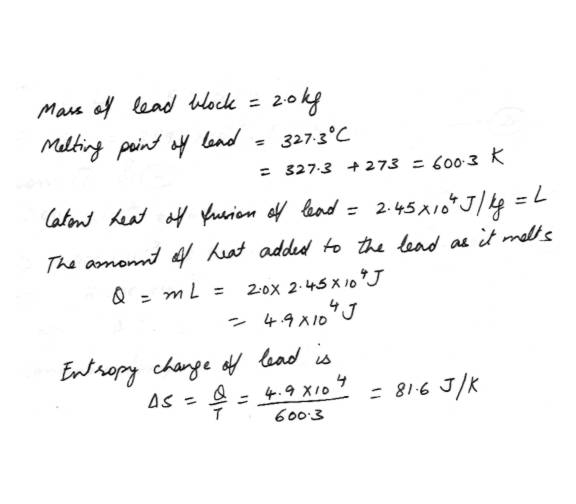
Physics Electrostatics Level: University
Potential EnergyCalculate the speed of (a) a proton and (b) an electron after each particle accelerates from rest through potential difference of 190V.

Physics Electrostatics Level: University
PotentialThe electric potential of a system as a function of position along the axis is given in figure 20-22. (a) In which of the regions 1,2,3 or 4 do you expect E sub x to be greatest. In which region does E sub x have its greatest magnitude .Explain. (b)Calculate the value of E sub x in each of the three regions 1, 2, 3, and 4 .

Physics Electrostatics Level: University
PotentialA typical 12-V car battery can deliver 7.5 x 10 to the 5th C of charge. If the energy supplied by the battery could be converted entirely to kinetic energy. What speed would it give to a 1200-kg car.

Physics Electrostatics Level: University
PotentialThe earth has an electric field with a magnitude of approximatly 100v/m near its surface. What is the potential difference between a point on the ground and a point on the same level as the top of the Washington Monument (555 ft high)
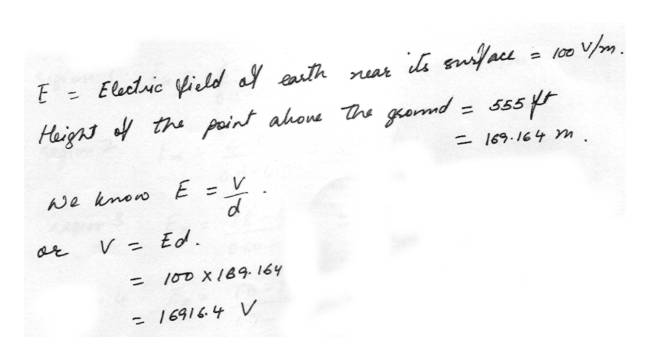
Physics Electrostatics Level: University
CapacitorNerve cells are long, thin cylinders along which electrical disturbances ( never impulses) travel. The cell membrane of a typical nerve cell consists of an inner and outer well separated by a distance of. 10 um. The electric field within the cell membrane is 7.0 x 10 to 5th N/C. Approximating the cell membrane as a parallel- plate capacitor determine the magnitude of the charge density on the inner and outer cell walls.
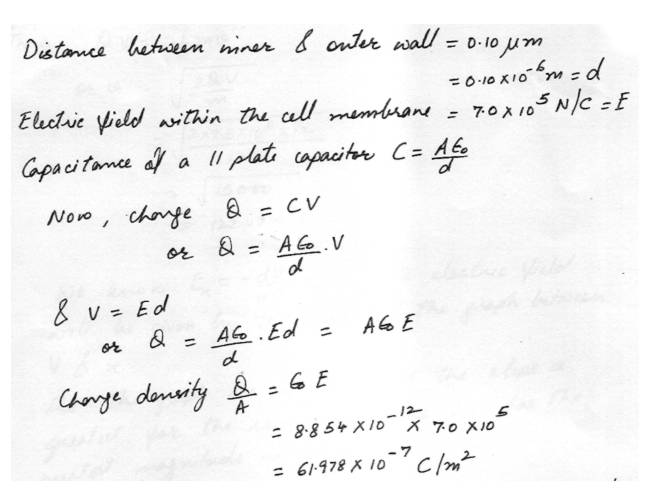
Physics Ray Optics Level: University
DiffractionA laser beam with wavelength of 632.8 nanometer shines at the normal incidence on the reflective side of a compact disc. The tracks of tiny pits in which information is coded onto the CD are 1.60 micrometer apart. For what angles of reflection ( measured from the normal) will the intensity of light be maximum?

Physics Ray Optics Level: University
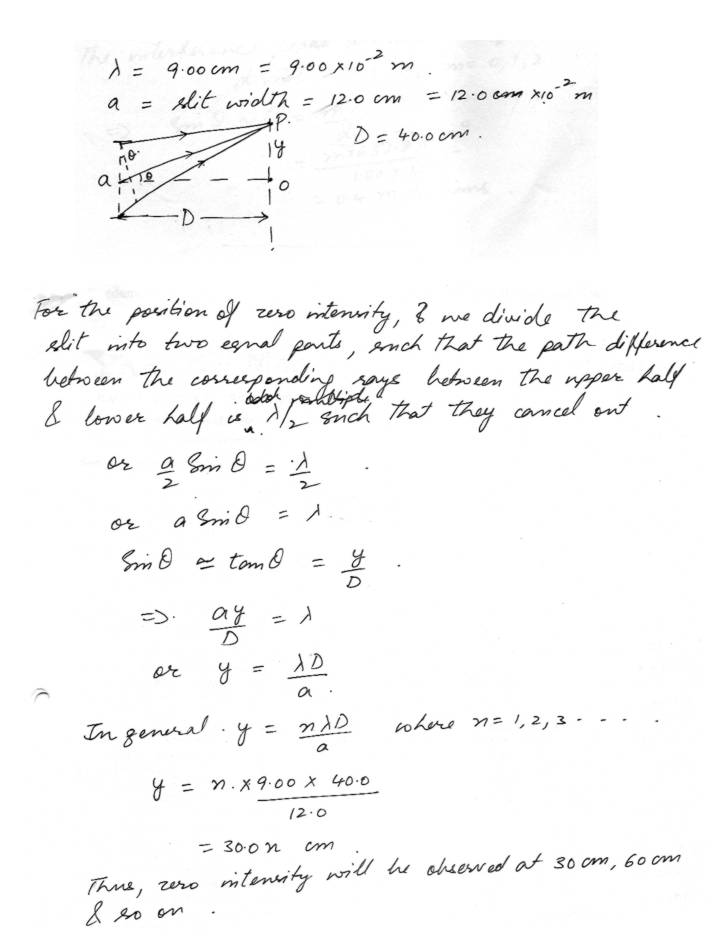
Wave opticsDiffraction occurs for all types of waves including sound waves high frequency sound from a distant source with a wavelength 9.00 cm passes through a narrow slit 12.0 cm wide. A microphone is placed 40.0 cm directly in front of the center of the slit corresponding to the O in the attachment. The microphone is then moved in a direction perpendicular to the line from the center of the slit to the point O. At what distances from O will the intensity detected by the microphone be zero.