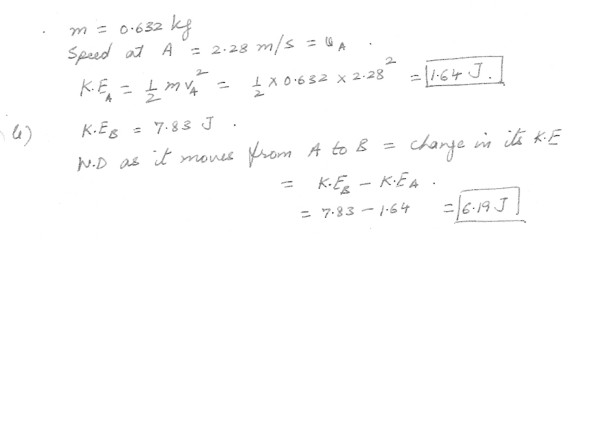Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
A child slides down a long slide in a playground . She starts from rest at a height h1 of 21.00 m . When she is patway down the slide , at a height h2 of 8.00 m , she is moving at a speed of 6.60 m/s . Calculate the mechanical energy lost due to friction (as heat, etc.)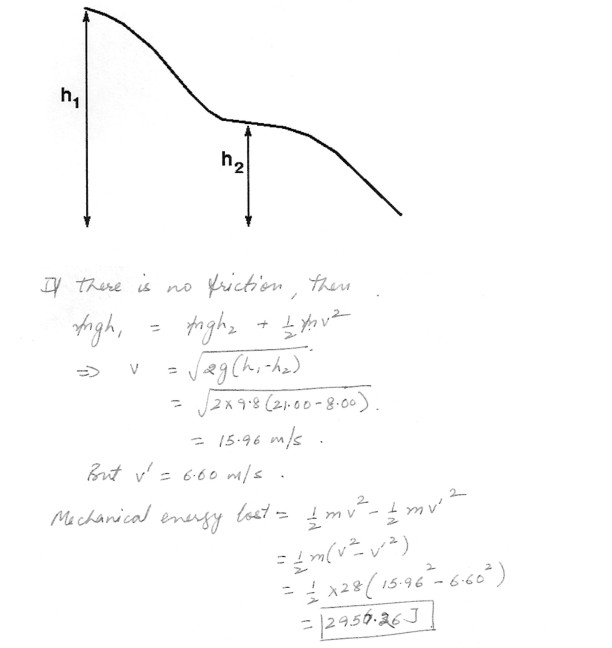
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
A 72.0 kg bungee jumper jumps from a bridge . She is tied to a 10.2 m long bungee cord and falls a total of 33.0 cm . Calculate the spring constant k of the bungee cord .
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
In the high jump , the kinetic energy of an athlete is transformed into gravitational potential energy without the aid of a pole . With what minimum speed must the athlete leave the ground in order to lift his center of mass 2.02 m and cross the bar with a speed of 0.680 m/s ?
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
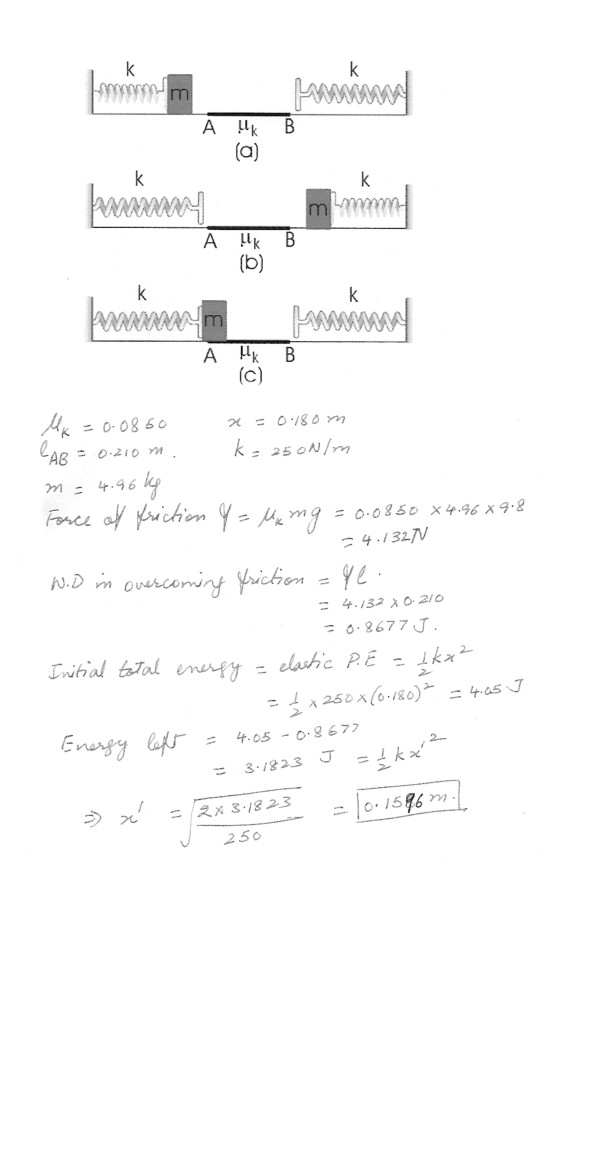
Two identical massless springs of constant k = 250 N/m are fixed at opposite ends of a level track , as shown in the figure at “click here”A 4.96 kg block I pressed against the left spring , compressing it by 0.180 m . The block (initially at rest) is then released, (a) The entire track is frictionless except for the section between A and B . Given that the coefficient of kinetic friction between block and track along AB is mu^k = 0.0850 , and given that the length AB is 0.210 m, determine the maximum compression of the spring on the right (b) .
Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: High School
(a) A 76.6 kg man steps out a window and falls (from rest) 1.01m to a sidewalk . What is his speed just before his feet strike the pavement ?
(b) If the man falls with his knees and ankles locked , the only cushion for his fall is a 0.490 cm give in the pads of his feet . Calculate the average force exerted on him by the ground in this situation . This average force is sufficient to cause cartilage damage in the joints or break bones .
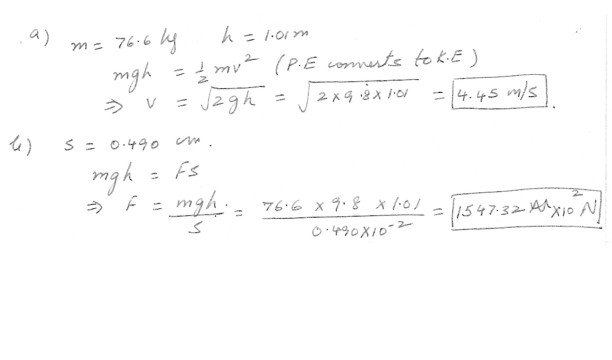
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
The figure at “click here” show masses sliding down a frictionless incline . All masses start from rest ; the mass of each block is given near the top of each figure , the height of the incline is given on the left , and the length of the incline is given on the right .Which of the following statements are true about the situation depicted in the figures .
The final velocity of the mass in picture B is greater than the one of the mass in picture F.
The final kinetic energy (when they reach the bottom of the incline ) is greater in picture A than in picture B .
The initial potential energy of the mass is greater in picture A than in picture E.
The larger the height of the incline , the larger the potential energy of the mass at the top of the incline .
Half-way down the incline , the potential energy is equal to half the total energy .

Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
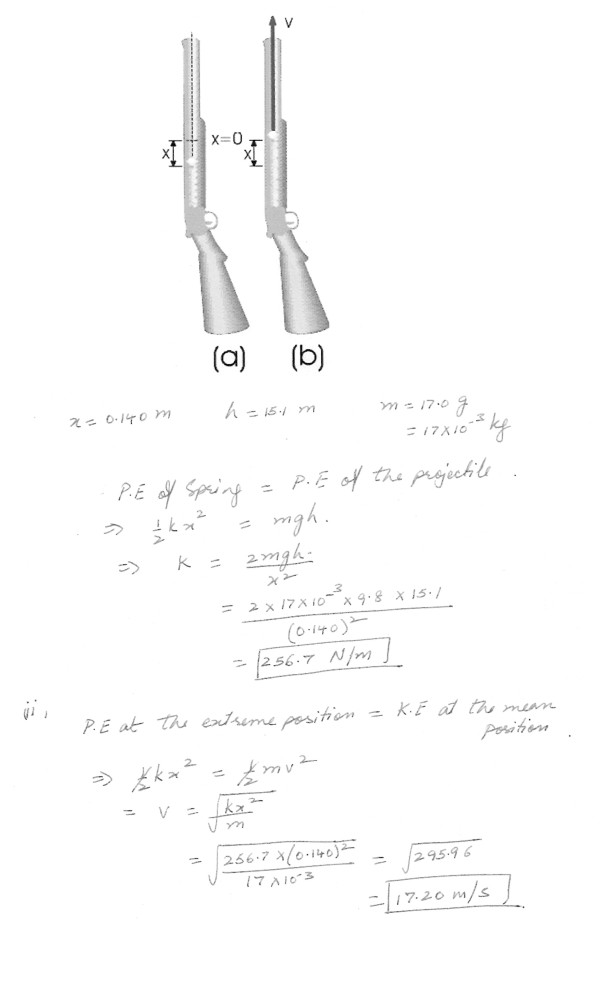
The launching mechanism of a toy gun of a spring of unknown spring constant , as shown in the figure at “click here” . If the spring is compressed a distance of 0.140 m and the gun fired vertically as shown in the figure at “click here” , the gun can launch a 17.0 g projectile from rest to a maximum height of 15.1 m above the string point of the projectile . Neglecting all resistive force ,(i) Determine the spring constant
(ii) Determine the speed of the projectile as it moves through the equilibrium position of the spring (where x = 0 )
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
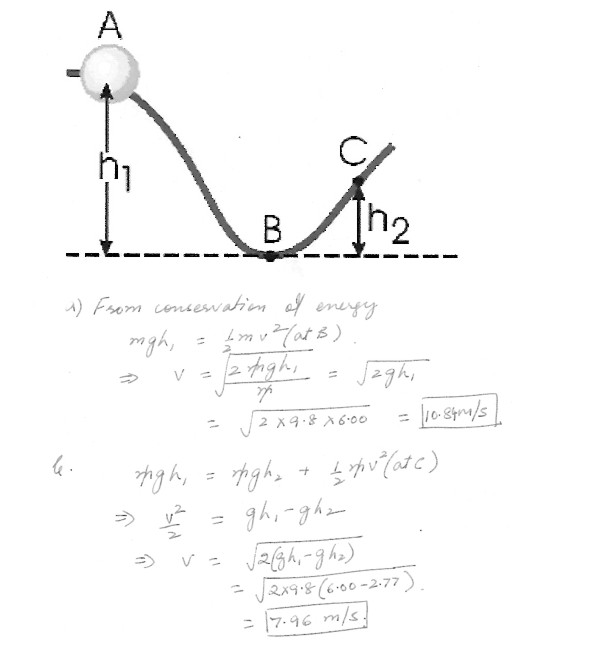
A 0.410 kg bead slides on a curved wire , starting from rest at point A as seen in the figure at ‘click here’ . Assume h1 = 6.00 m and h2 = 2.77 m . If the wire is frictionless(a) Find the speed of the bead at B .
(b) If wire is frictionless , find the speed of the bead at C .
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
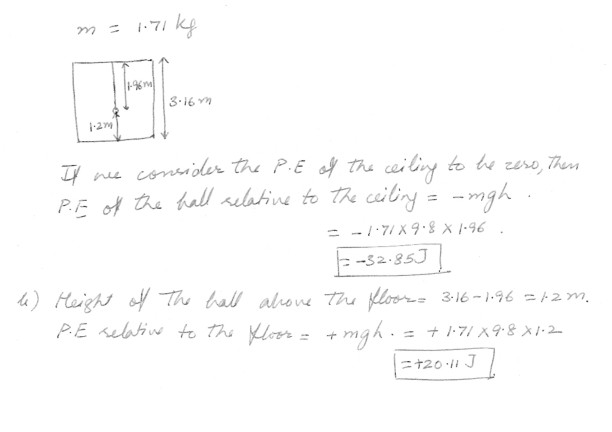
A 1.71 kg ball is attached to a ceiling by a 1.96 m long string . The height of the room is 3.16 m .a) What is the gravitational potential energy of the ball relative to the ceiling ?
b) What is the gravitational potential energy of the ball relative to the floor ?
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
How long will it take a 1750 W motor to lift a 272 kg piano to a sixth-story window 13.6 m above ?
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
A 50.3 kg student climbs a 5.10 m long rope and stops at the top .a) What must her average speed in order to match the power output of a 120 W lightbulb ?
b) How much work does she do ?

Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
A 77.9 g arrow is fired from a bow whose string exerts an average force of 99.8 N on the arrow over a distance of 79.2 cm . What is the speed of the arrow as it leaves the bow ?
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
On a frozen pond , a 14.1 kg sled is given a kick that imparts to it an initial speed of Vo = 1.70 m/s . The coefficient of kinetic friction between sled and ice is mu^k = 0.105 . Use the work kinetic energy theorem to find the distance the sled moves before coming to rest .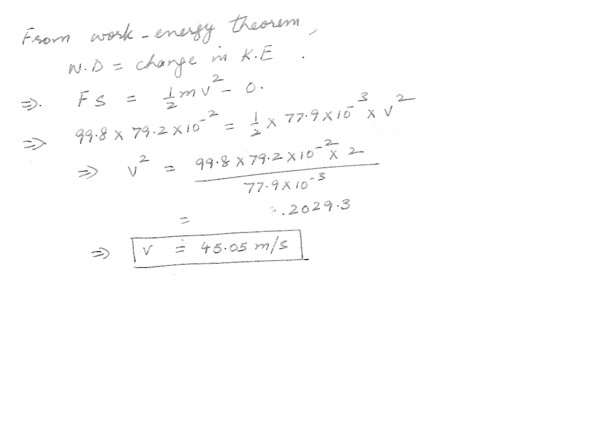
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
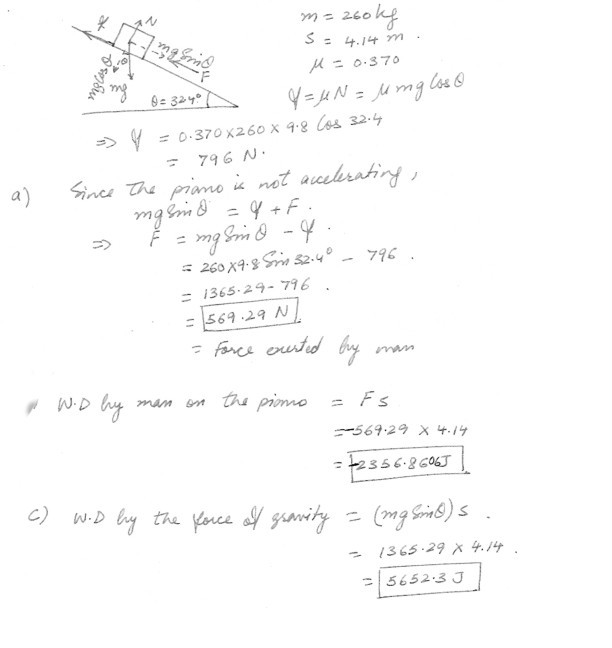
A 260 kg piano slides 4.14 m down a 32.4 degree incline and is kept from accelerating by a man who is pushing back on it parallel to the incline. As seen in the figure at “click here” . The effective coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.370a). Calculate the work done by the man on the piano .
b). Calculate the work done by the force of gravity.
c). Calculate the work done by the force of gravity .
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
Particle in motion
A 0.632 kg particle has a speed of 2.28 m/s at point A and kinetic energy of 7.83 J at point B .a) What is its kinetic energy at A ?
b) What is the total work done on the particle as it move from A to B ?