Physics Rotational Mechanics Level: High School
A wheel (radius = 0.20 m) is mounted on a frictionless . horizontal axle . A light rope wrapped around the wheel supports a 0.50 kg object as shown below . When released from rest , the object falls with a downward acceleration of 5.0 m/s^2 . What is the moment of inertia of the wheel ? Diagram of a wheel .a. 0.023 kg-m2
b. 0.027 kg-m2
c. 0.016 kg-m2
d. 0.019 kg-m2
e. 0.032 kg-m2

Physics Rotational Mechanics Level: High School
A flywheel in the form of a heavy circular disk of diameter 0.600 meters and mass 200 kg is mounted on a frictionless bearing . A motor connected to the flywheel accelerates it from rest to 1000 revolution/minute . How work is done on it during this acceleration ?a. 20.2 k Joules
b. 15.3 k Joules
c. 49.3 k Joules
d. 67.3 k Joules
e. 89.7 k Joules

Physics Rotational Mechanics Level: High School
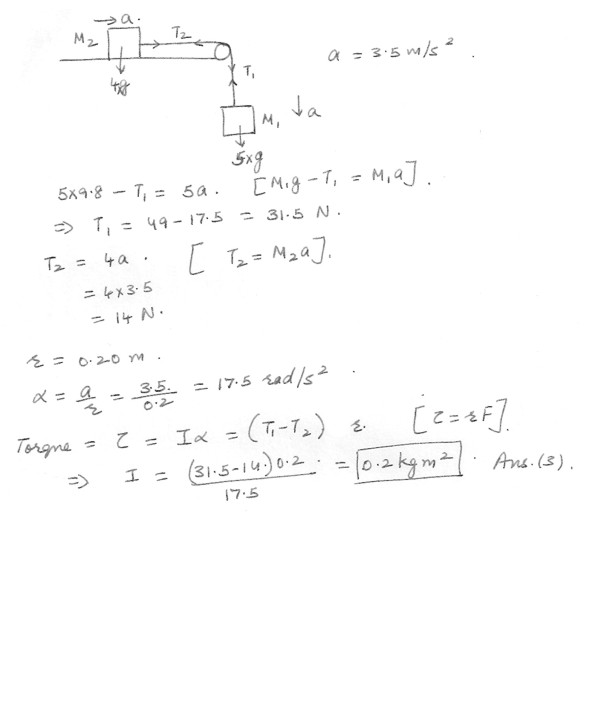
A mass (M1 = 5.0 kg ) is connected by a light rope to a mass (M2 = 4.0 kg ) which slide on smoothly . The pulley (radius = 0.20 meter ) rotates about a frictionless axle . The acceleration of M2 is 3.5 m/s2 . What is the moment of inertia of pulley ? Diagram of a mass .a. 0.29 kg-m2
b. 0.42 kg-m2
c. 0.20 kg-m2
d. 0.62 kg-m2
e. 0.60 kg-m2
Physics Rotational Mechanics Level: High School
A wheel rotates about a fixed axis with an angular velocity of 20 rad/s . During a 5.0 second time interval, the angular velocity increases to 40 rad/s. Assume that the angular acceleration was constant during the 5.0 second interval. How many revolutions does the wheel turn during through during the 5.0 second interval ?a. 20 revolutions
b. 24 revolutions
c. 32 revolutions
d. 28 revolutions
e. 39 revolutions

Physics Rotational Mechanics Level: High School
A wheel rotating about a fixed axis with a constant angular acceleration of 2.0 rad/s2. turns through 2.4 revolutions during a 2.0 seconds time interval. What was the angular velocity omega at the end of this time interval ?a. 9.5 rad/s
b. 9.7 rad/s
c. 9.3 rad/s
d. 9.1 rad/s
e. 8.8 rad/s
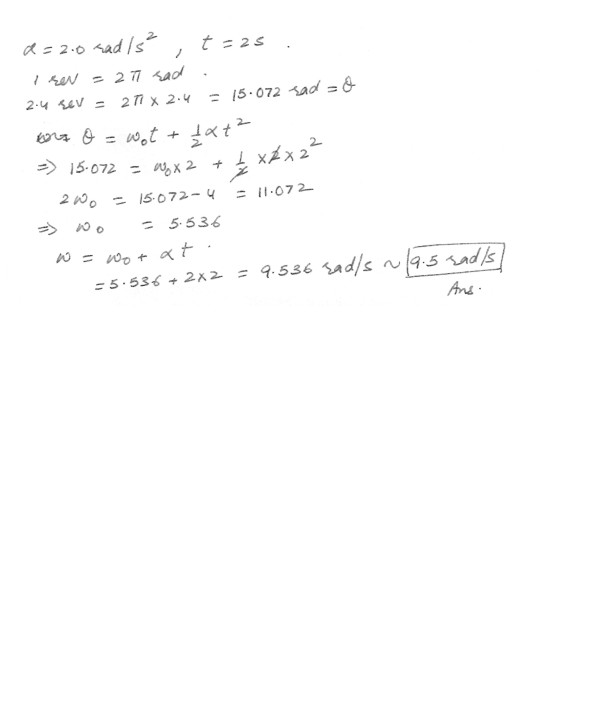
Physics Rotational Mechanics Level: High School
At t = 0 , a wheel rotating about a fixed axis at a constant angular acceleration of 2.0 rad/s2 turns through 2.4 revolution during a 2.0 seconds time interval . What was the angular velocity omega at the end of this time interval ?.9 rad
b. 4.7 rad
c. 4.5 rad
d. 4.3 rad
e. 4.1 rad

Physics Rotational Mechanics Level: High School
Centre of Mass
Three particles are placed in the x-y plane . A 40 g particle is located at (3,4) meters, and a 50 g particle is positioned at (-2, -6) meter . Where must a 20 g particle be placed so that the center of mass of this three –particle system is located at the origin ?a. (-1, -3) meter
b. (-1, +2) meter
c. (-1, +12) meter
d. (-1, +7) meter
e. (-1, +3) meter

Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: High School
Conservation of momentum
A 2.0 kg mass sliding on a frictionless surface explode into two 1.0 kg masses . After the explosion the velocities of the masses are (1) 3.0 m/s, north and (2) 5.0 m/s, 30 degree north of east . What was the magnitude of the original velocity of the 2.0 kilogram mass ?a. 3.1 m/s
b. 3.9 m/s
c. 3.5 m/s
d. 2.8 m/s
e. 2.4 m/s

Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
A 6.0 kg object, initially at rest in outer space , “explodes “ into three segments of equal mass . Two of these elements are observed to be moving with equal speeds of 20 m/s with an angle of 60 degree between their direction of motion . How much kinetic energy is released in this explosion ?a. 2.4 k Joules
b. 2.9 k Joules
c. 2.0 k Joules
d. 3.4 k Joules
e. 1.2 k Joules

Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: High School
Conservation of momentum
A 5.0 g particle moving 60 m/s collides with a 2.0 g particle initially at rest . After the collision each of the particles has a velocity that is directed 30 degree from the original direction of motion of the 5.0 g particle . What is the speed of the 2.0 g particle after the collision ?a. 72 m/s
b. 79 m/s
c. 79 m/s
d. 94 m/s
e. 67 m/s

Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
A 2.0 kg kilogram object moving with a velocity of 5.0 m/s in the positive x direction strikes and sticks to a 3.0 kg object moving with a speed of 2.0 m/s in the same direction . How much kinetic energy is lost in this collision ?1. 2.4 Joules
2. 9.6 Joules
3. 5.4 Joules
4. 0.6 Joules
5. 6.0 Joules

Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: High School
A car with mass m = 1200 kg is initially traveling directly east with a speed vi = 25.0 m/s . It crashes into the rear end of a truck with mass M = 9000 kg moving in the same direction with speed 20.0 m/s . Immediately after the collision, the car has a speed vf = 18.0 m/s in its original direction . What is the velocity of the truck immediately after the collision ?1. 15.0 m/s
2. 10.0 m/s
3. 5.0 m/s
4. 20.9 m/s
5. 18.0 m/s

Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: High School
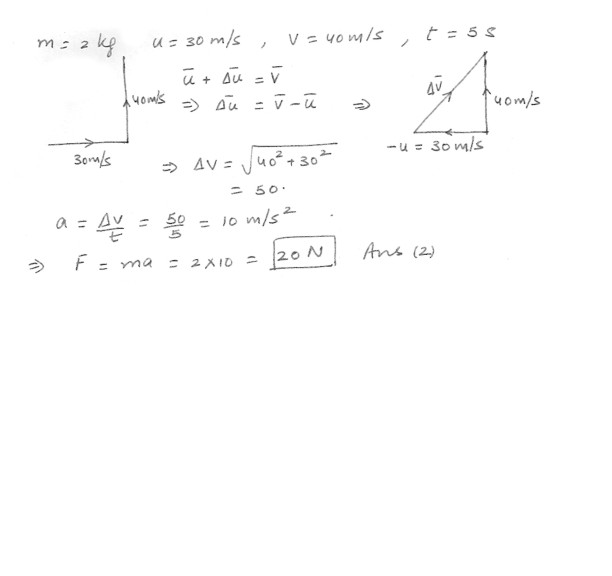
The speed of a 2.0 kilogram object changes from 30 m/s to 40 m/s during a 5.0 second time interval . During this same time interval , the velocity of the object changes its direction by 90 degree . What is the Magnitude of the average total force acting on the object during this time interval ?30 Newtons
20 Newtons
40 Newtons
50 Newtons
4 Newtons
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
A women does 200 J of work to move a table 4m across the floor . What is the magnitude of the force that the women applied to the table if this force is applied in the horizontal direction ?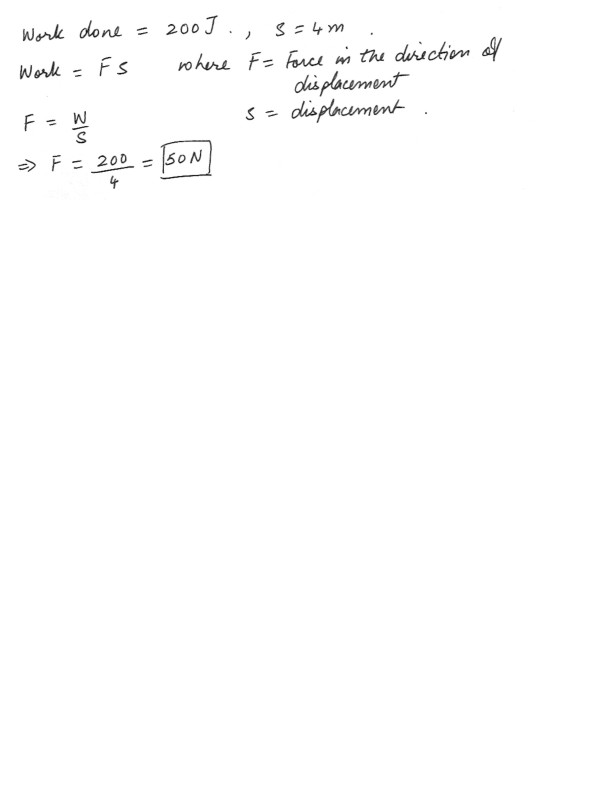
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
A child pulls a block across the floor with force applied by a horizontal held string . A smaller frictional force also acts upon the black , yielding a net force on the block that is smaller than the force applied by the string . Does the work done by the force applied by the string equal the change in kinetic energy in this situation ? Explain .
