Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
A shot-putter accelerates a 7.46 kg shot from rest to 13.8 m/s . If this motion takes 1.96 s , what average power was developed ?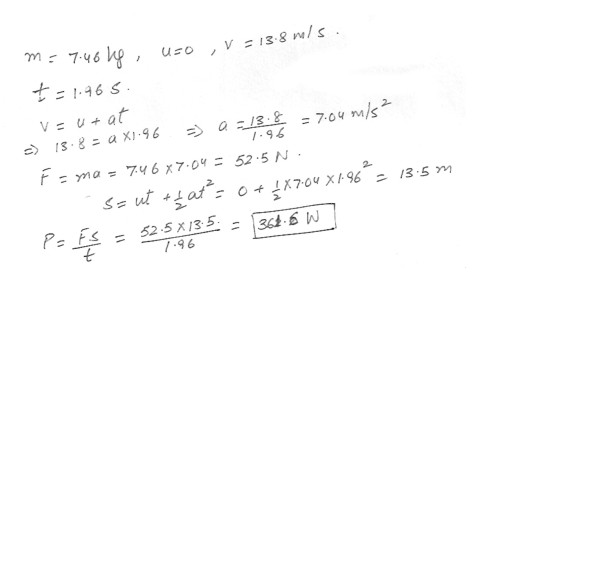
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
A 19.6 kg child descends a slide 3.20 m high and reaches the bottom with a speed of 2.30 m/s . How much thermal energy due to friction was generated in this process ?
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
A 74.8kg bungee jumper jumps from a bridge . She is tied to a 12.4 m long bungee cord and falls a total of 33.4 m . Calculate the spring constant k of the bungee cord .(a) Calculate the maximum acceleration experienced by the jumper .

Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
In the high jump , the kinetic energy of an athlete is transformed into potential energy without the aid of a pole . With what minimum speed must the athlete leave the ground in order to lift his center of mass 2.16 m and cross the bar with a speed of 0.700 m/s ?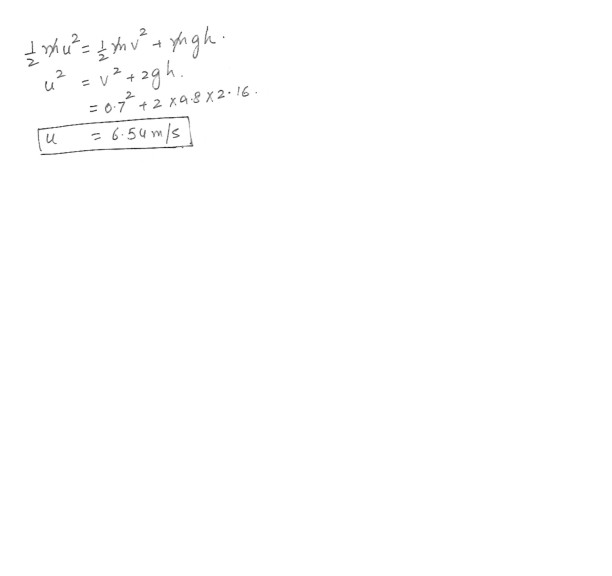
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
In starting an exercise , a 1.72 m tall person lifts a 2.46 kg book on the ground so it is 2.33 m above the ground . What is the potential energy of the book relative to the ground ?(a) What is the potential energy of the book relative to the top of the persons head ?
(b) Calculate the work done by the person .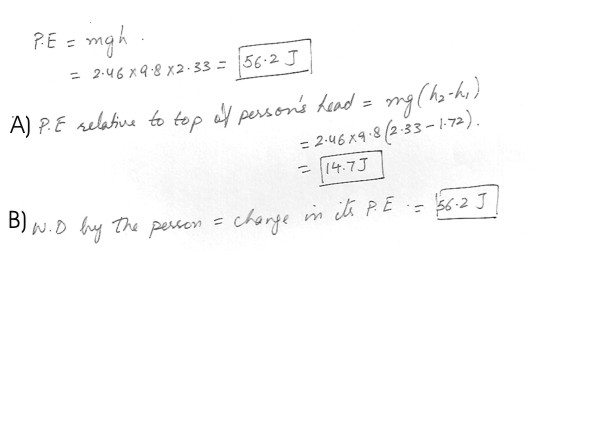
Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: High School
A softball having a mass of 0.240 kg is pitched at 92.0 km/hr . By the time it reaches the plate , it may have slowed by 12.2 percent . Neglecting gravity , estimate the average force of air resistance during a pitch , if the distance between the plate and the pitcher is 15.3 m .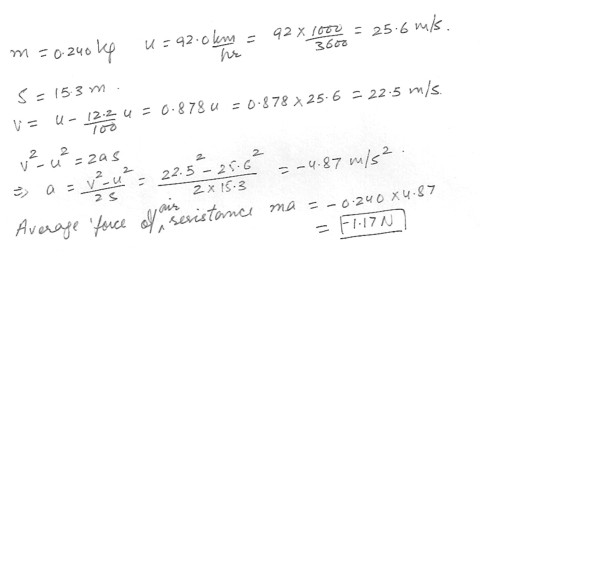
Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: High School
An 77.5 g arrow is fired from a bow whose string exerts an average force of 98.9 N on the arrow over a distance of 78.4 cm , What is the speed of the arrow as it leaves the bow ?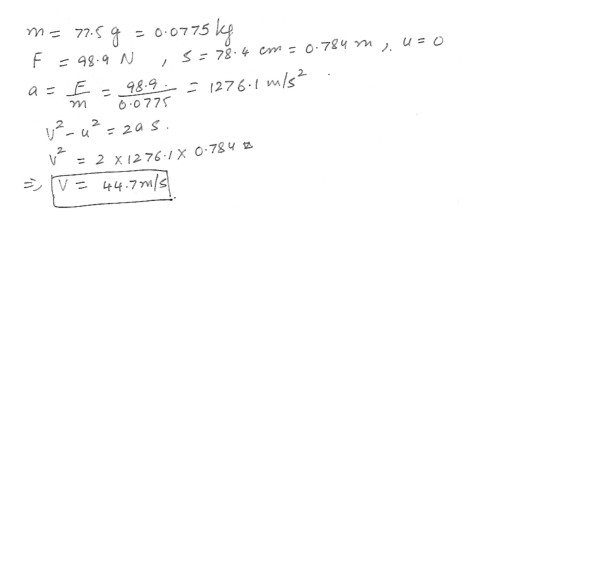
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
A spring has k = 92.8 N/m . Determine the work needed to stretch it from x = 3.58 cm to x = 5.88 cm, where x is the displacement from its unstretched length .
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
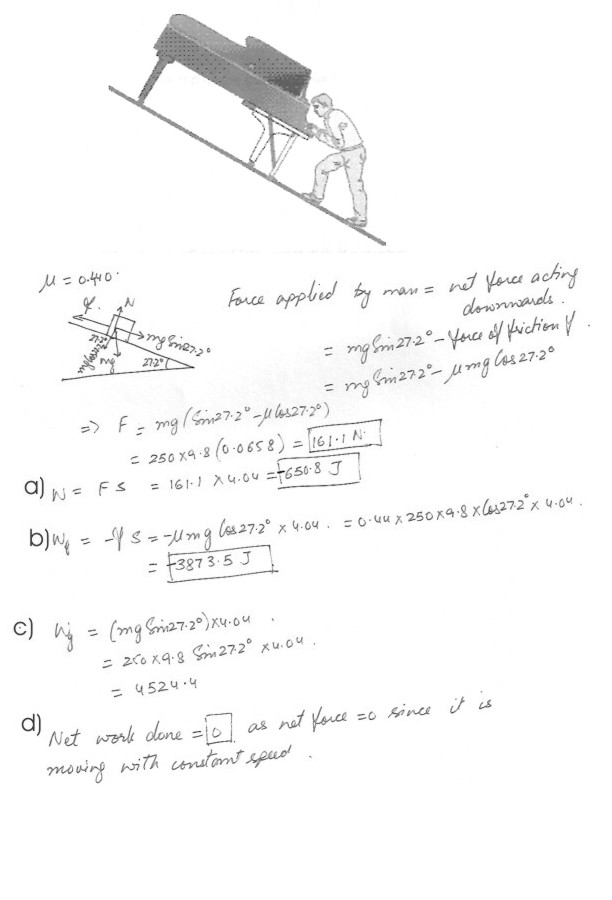
A 250 kg piano slides 4.04 m down a 27.2 degree incline and is kept from accelerating by a man who is pushing back on it parallel to the incline , as seen in the figure at “click here” , The effective coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.440 . Calculate the force exerted by the man .(a) Calculate the work done by the man on the piano
(b) Calculate the work done by the friction force
(c) Calculate the work done by the force of gravity
(d) Calculate the net work done on the piano
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
A 945 crate rests on the floor . How much work is required to move it at constant speed ?(a) How much work is required to move it at constant speed 5.20 m vertically ?

Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: High School
Conservation of momentum
The result of a collision experiment performed by a group of students (on a horizontal frictional surface ) is summarized on a Displacement versus Time graph shown below .(a) By analyzing the graph , describe (in written statements) the collision of the objects . Sketch the collision diagram .
(b) Use data from the graph to prove that the momentum is conserved during the above collision. Identify the physical quantities and specify directions .
(c) Is the collision elastic or inelastic ? Prove your answer mathematically .
(d) Conclusion .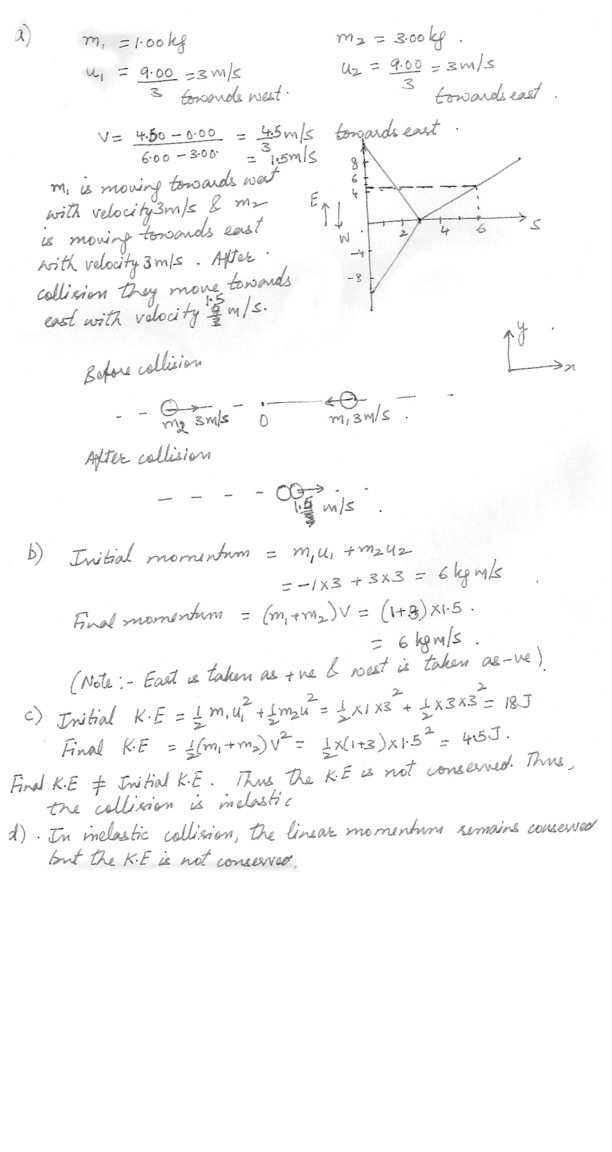
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
A motorcyclist (with combined mass of 200.0 kg ) heads east at a constant speed of 20.0 m/s as shown in the diagram at “click here” . Right before he enters the curve (position A) the mechanical system in the motorcycle breaks down . The motorcyclist leaves the curve at a speed of 5.40 m/s (position B) and continues to move south on a frictionless surface for a distance of 100.00 m when he hits a vertical cement block (position C)(a) Using the information provided and the corresponding laws of Physics describes, in detail , the motion of the motorcyclist between position A and C .
(b) Calculate the magnitude of the frictional force acting on the motorcycle between position A and B . Explain your reasoning .
(c) How much is the change in kinetic energy between position B and C ? What is the energy converted to at the moment of impact ?
(d) If the duration of the impact is 0.0100 s , What is the magnitude of the force exerted by the cement block on the motorcycle /passenger system ? Could a passenger survive this accident ? Explain your answer ?
(e) What magnitude of frictional force would be needed to stop the motorcycle right before impact with the cement block ?
Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: High School
Conservation of momentum
A helium atom (mass 4.0 u ) moving at 600.0 m/s to the right collides with an oxygen molecule (mass 32 u) moving in the same direction at 400.0 m/s . After the collision, the oxygen molecule moves at 500.0 m/s to the right . What is the velocity of the helium atom after the collision ?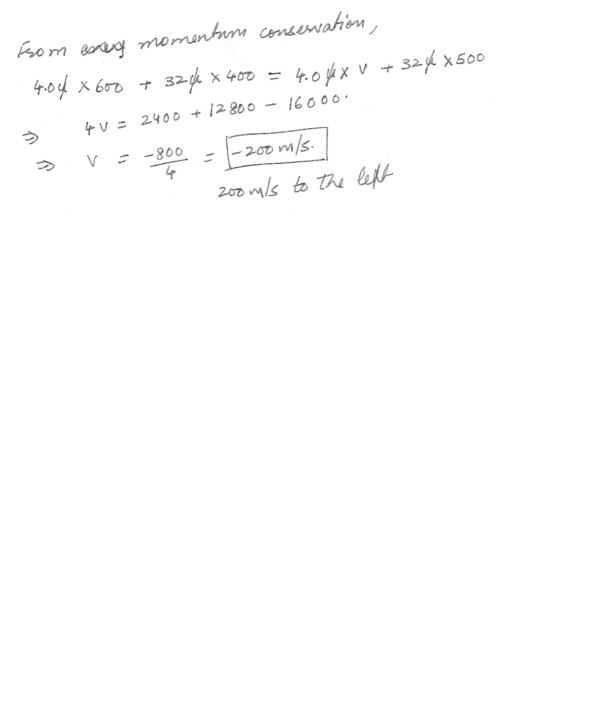
Physics Work,Power & Energy Level: High School
Two identical gliders on an air track are held together by a piece of string , compressing the spring between the gliders. While they are moving to the right at a common speed of 0.50 m/s , someone holds a match under the string and burns it , letting the spring force of the gliders slide apart. One glider is then observed to be moving to the right at 1.30 m/s .(a) What velocity does the other glider have ?
(b) If the total kinetic energy of the two gliders after the collision greater than , less then or equal to the total kinetic energy before the collision ? If greater , where did the extra energy come from ? If less , where did the “lost energy” go ?

Physics Force & Laws Of Motion Level: High School
Conservation of momentum
In the railroad freight yard , an empty freight car of mass m rolls along a straight level track at 1.0 m/s and collides with an initially stationary , fully loaded completion .(a) What is the speed of the two cars after collision ?
(b) Suppose instead that two cars rest after collision . with what was the speed was the fully loaded boxcar moving before the collision if the empty one was moving at 1.0 m/s ?

